Robust high-performance data storage through magnetic anisotropy
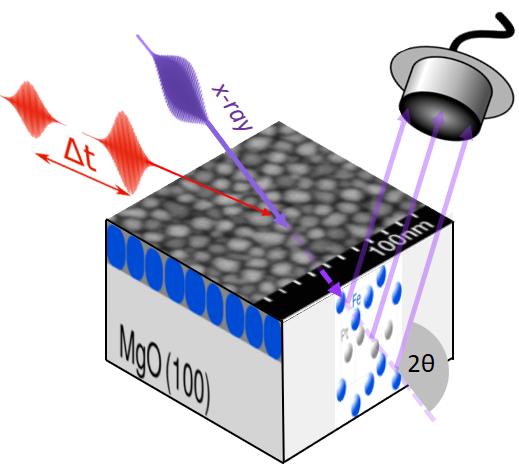
This is how the experiment went: Two laser pulses hit the thin film of iron-platinum nanoparticles at short intervals: The first laser pulse destroys the spin order, while the second laser pulse excites the now unmagnetised sample. An X-ray pulse then determines how the lattice expands or contracts. Credit: M. Bargheer/ Uni Potsdam
A team led by Prof. Matias Bargheer has now experimentally compared this fascinating phenomenon for the first time on different iron-platinum thin films. Bargheer heads a joint research group at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and the University of Potsdam.
Together with colleagues from Lyon, Brno and Chemnitz, he wanted to investigate how the behavior of perfectly crystalline FePt layers differs from the FePt thin films used for HAMR memories. These consist of crystalline nanograins of stacked monatomic layers of iron and platinum embedded in a carbon matrix.
The samples were locally heated and excited with two laser pulses in quick succession and then measured by X-ray diffraction to determine how strongly the crystal lattice expands or contracts locally.
“We were surprised to find that the continuous crystalline layers expand when heated briefly with laser light, while loosely arranged nano grains contract in the same crystal orientation,” explains Bargheer.
“HAMR data memories, on the other hand, whose nano-grains are embedded in a carbon matrix and grown on a substrate react much weaker to laser excitation: They first contract slightly and then expand slightly.”
“Through these experiments with ultrashort X-ray pulses, we have been able to determine how important the morphology of such thin films is,” says Alexander von Reppert, first author of the study and PhD student in Bargheer's group. The secret is transverse contraction, also known as the Poisson effect.
“Everyone who has ever pressed firmly on an eraser knows this,” says Bargheer. “The rubber gets thicker in the middle.” And Reppert adds: “The nanoparticles can do that too, whereas in the perfect film there is no room for expansion in the plane, which would have to go along with the spin driven contraction perpendicular to the film.”
So FePt, embedded in a carbon matrix, is a very special material. It not only has exceptionally robust magnetic properties. Its thermomechanical properties also prevent excessive tension from being created when heated, which would destroy the material – and that is important for HAMR!
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from…

A new way of entangling light and sound
For a wide variety of emerging quantum technologies, such as secure quantum communications and quantum computing, quantum entanglement is a prerequisite. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for the Science of Light…

Telescope for NASA’s Roman Mission complete, delivered to Goddard
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is one giant step closer to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. The mission has now received its final major delivery: the Optical Telescope…



