New optical computing approach offers ultrafast processing
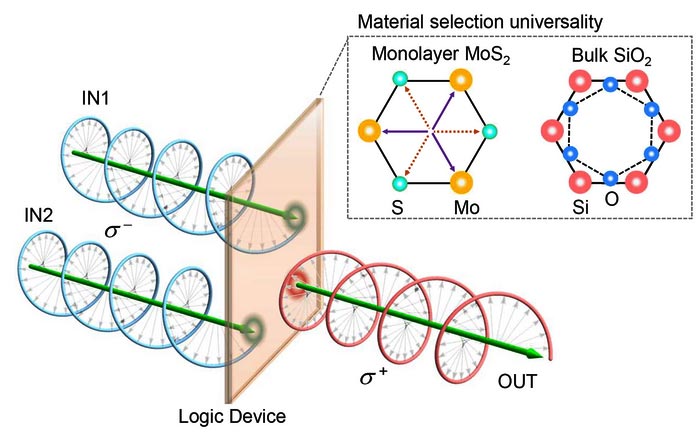
The optical chirality logic gate is made of a material which emit lights with different circular polarization depending on the chirality of the input beams.
Credit: Yi Zhang / Aalto University
Processing devices based on polarized light run one million times faster than current technology.
Logic gates are the fundamental components of computer processors. Conventional logic gates are electronic – they work by shuffling around electrons – but scientists have been developing light-based optical logic gates to meet the data processing and transfer demands of next-generation computing. New optical chirality logic gates developed by researchers at Aalto University operate about a million times faster than existing technologies, offering ultrafast processing speeds.
The new approach uses circularly polarized light as the input signal. The logic gates are made from crystalline materials that are sensitive to the handedness of a circularly polarized light beam – that is, the light emitted by the crystal depends on the handedness of the input beams. This serves as the basic building block for one type of logic gate (XNOR), and the remaining types of logic gates are built by adding filters or other optical components.
The team also showed that a single device could contain all of their chirality logic gates operating simultaneously in parallel. This is a significant advance over existing logic gates, which can only carry out a single logic operation at a time. Simultaneous parallel logic gates could be used to build complex, multifunctional logic circuits. Finally, the team demonstrated that the chirality logic gate could be controlled and configured electronically, a necessary step for hybrid electrical/optical computing.
Journal: Science Advances
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq8246
Article Title: Chirality Logic Gates
Article Publication Date: 9-Dec-2022
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



