A step closer to single-atom data storage
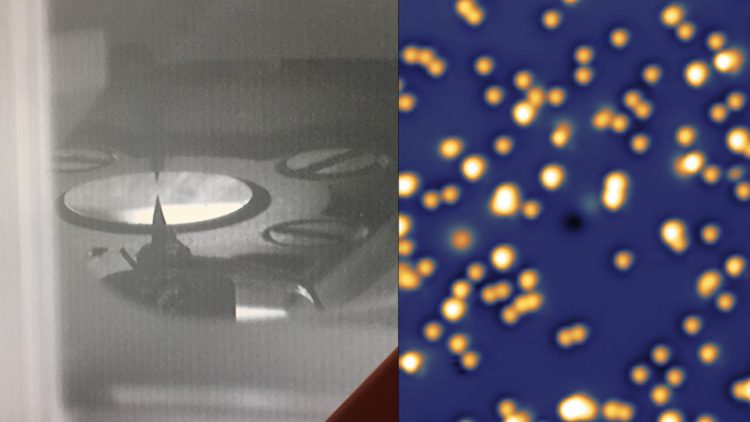
LEFT: STM image of Holmium single atom magnets. RIGHT: and Cobalt helper atoms on magnesium oxide. Credit: F. Natterer/EPFL
One of these are single-atom magnets: storage devices consisting of individual atoms stuck (“adsorbed”) on a surface, each atom able to store a single bit of data that can be written and read using quantum mechanics. And because atoms are tiny enough to be packed together densely, single-atom storage devices promise enormous data capacities.
But although they are no longer science fiction, single-atom magnets are still in basic research, with many fundamental obstacles to be overcome before they can be implemented into commercial devices. EPFL has been at the forefront of the field, overcoming the issue of magnetic remanence, and showing that single-atom magnets can be used to read and write data.
In a new study published in Physical Review Letters, physicists at EPFL's Institute of Physics have used Scanning Tunneling Microscopy to demonstrate the stability of a magnet consisting of a single atom of holmium, an element they have been working with for years.
“Single-atom magnets offer an interesting perspective because quantum mechanics may offer shortcuts across their stability barriers that we could exploit in the future,” says EPFL's Fabian Natterer who is the paper's first author. “This would be the last piece of the puzzle to atomic data recording.”
The scientists exposed the atom to extreme conditions that normally de-magnetize single-atom magnets, such as temperature and high magnetic fields, all of which would pose risks to future storage devices.
Using a Scanning Tunneling Microscope, which can “see” atoms on surfaces, the scientists found that the holmium atoms could retain their magnetization in a magnetic field exceeding 8 Tesla, which is around the strength of magnets used in the Large Hadron Collider. The authors describe this as “record-breaking coercivity”, a term that describes the ability of a magnet to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming demagnetized.
Next, they turned up the heat: The researchers exposed a series of Holmium single-atom magnets to temperatures of up to 45 Kelvin, (-233.15 degrees Celsius), which, for single atoms, is like being in a sauna. The Holmium single-atom magnets remained stable up to a temperature of 35K. Only at around 45K, the magnets began to spontaneously align themselves to the applied magnetic field. This showed that they can withstand relatively high temperature perturbations and might point to the way forward for running single-atom magnets at more commercially viable temperatures.
“Research in the miniaturization of magnetic bits has focused heavily on magnetic bistability,” says Natterer. “We have demonstrated that the smallest bits can indeed be extremely stable, but next we need to learn how to write information to those bits more effectively to overcome the magnetic 'trilemma' of magnetic recording: stability, writability, and signal-to-noise ratio.”
###
Other contributors
Institute for Basic Science (Korea)
Ewha Womans University (Korea)
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.027201All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



