AI Tool Analyzes Speech Patterns to Identify Depression

Evaluation of an AI-based voice biomarker tool to detect signals consistent with moderate to severe depression
Background and Goal: Depression impacts an estimated 18 million Americans each year, yet depression screening rarely occurs in the outpatient setting. This study evaluated an AI-based machine learning biomarker tool that uses speech patterns to detect moderate to severe depression, aiming to improve access to screening in primary care settings.
Study Approach: The study analyzed over 14,000 voice samples from U.S. and Canadian adults. Participants answered the question, “How was your day?” with at least 25 seconds of free-form speech. The tool analyzed vocal biomarkers associated with depression, including speech cadence, hesitations, pauses, and other acoustic features. These were compared to results from the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), a standard depression screening tool. A PHQ-9 score of 10 or higher indicated moderate to severe depression. The AI tool provided three outputs: Signs of Depression Detected, Signs of Depression Not Detected, and Further Evaluation Recommended (for uncertain cases).
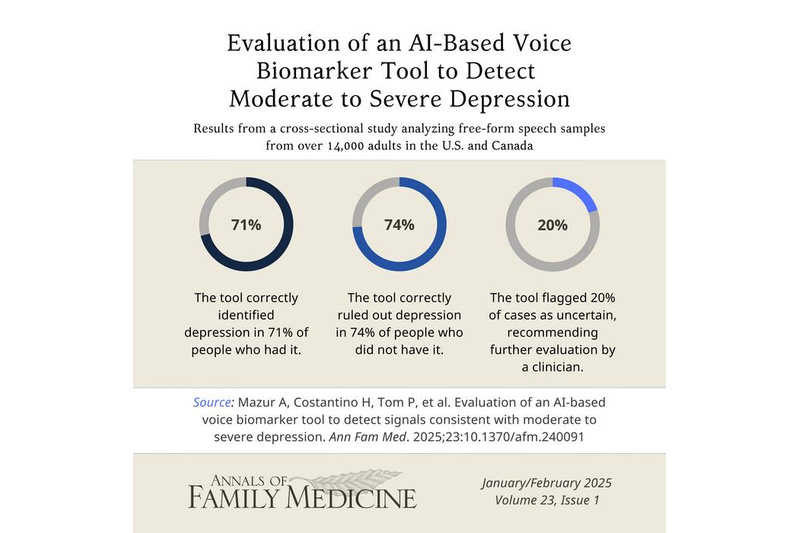
Main Results: The dataset used to train the AI model consisted of 10,442 samples, while an additional 4,456 samples were used in a validation set to assess its accuracy.
Why It Matters: The study findings suggest that machine learning technology could serve as a complementary decision-support tool for assessing depression.
Evaluation of an AI-Based Voice Biomarker Tool to Detect Signals Consistent With Moderate to Severe Depression
Alexa Mazur, BA, et al
Kintsugi Mindful Wellness, Inc, San Francisco, California
Original Publication
, , , and
Journal: The Annals of Family Medicine
Article Title: Evaluation of an AI-Based Voice Biomarker Tool to Detect Signals Consistent With Moderate to Severe Depression
Article Publication Date: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.240091
Media Contact
Deb Hipp
American Academy of Family Physicians
debhipp24@gmail.com
Source: EurekAlert!
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

New Study Offers Hope for Chronic Pain Relief in Dialysis Patients
People undergoing hemodialysis treatment for kidney failure often experience chronic pain related to their condition, but it can be difficult to manage with opioid medication and other conventional treatments. A…

Early Adult Mortality Surges in Post-COVID US
New research from Boston University School of Public Health and the University of Minnesota shows that death rates for early adults, or adults aged 25-44, rose sharply during the COVID-19…

Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries Boosts Supply Chain Resilience
Recycling lithium-ion batteries to recover their critical metals has significantly lower environmental impacts than mining virgin metals, according to a new Stanford University lifecycle analysis published in Nature Communications. On…



