Artificial intelligence can identify microscopic marine organisms
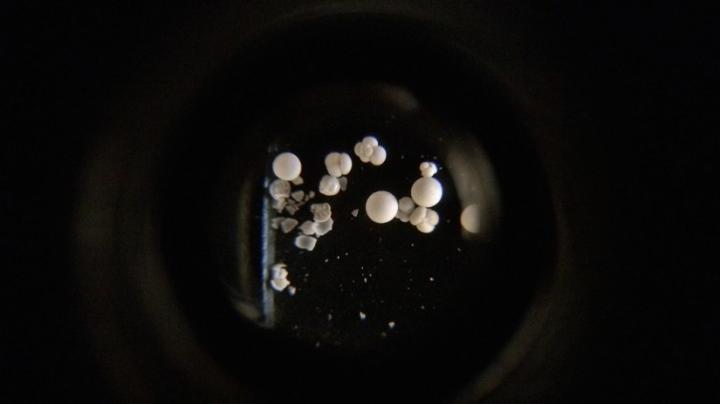
Foraminifera, or forams, as seen through the viewfinder of a microscope. Credit: Tom Marchitto
Specifically, the AI program has proven capable of identifying six species of foraminifera, or forams – organisms that have been prevalent in Earth's oceans for more than 100 million years.
Forams are protists, neither plant nor animal. When they die, they leave behind their tiny shells, most less than a millimeter wide. These shells give scientists insights into the characteristics of the oceans as they existed when the forams were alive.
For example, different types of foram species thrive in different kinds of ocean environments, and chemical measurements can tell scientists about everything from the ocean's chemistry to its temperature when the shell was being formed.
However, evaluating those foram shells and fossils is both tedious and time consuming. That's why an interdisciplinary team of researchers, with expertise ranging from robotics to paleoceanography, is working to automate the process.
“At this point, the AI correctly identifies the forams about 80 percent of the time, which is better than most trained humans,” says Edgar Lobaton, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at North Carolina State University and co-author of a paper on the work.
“But this is only the proof of concept. We expect the system to improve over time, because machine learning means the program will get more accurate and more consistent with every iteration. We also plan to expand the AI's purview, so that it can identify at least 35 species of forams, rather than the current six.”
The current system works by placing a foram under a microscope capable of taking photographs. An LED ring shines light onto the foram from 16 directions – one at a time – while taking an image of the foram with each change in light. These 16 images are combined to provide as much geometric information as possible about the foram's shape. The AI then uses this information to identify the foram's species.
The scanning and identification takes only seconds, and is already as fast – or faster – than the fastest human experts.
“Plus, the AI doesn't get tired or bored,” Lobaton says. “This work demonstrates the successful first step toward building a robotic platform that will be able to identify, pick and sort forams automatically.”
Lobaton and his collaborators have received a grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF), starting in January 2019, to build the fully-functional robotic system.
“This work is important because oceans cover about 70 percent of Earth's surface and play an enormous role in its climate,” says Tom Marchitto, an associate professor of geological sciences at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and corresponding author of the paper.
“Forams are ubiquitous in our oceans, and the chemistry of their shells records the physical and chemical characteristics of the waters that they grew in. These tiny organisms bear witness to past properties like temperature, salinity, acidity and nutrient concentrations. In turn we can use those properties to reconstruct ocean circulation and heat transport during past climate events.
“This matters because humanity is in the midst of an unintentional, global-scale climate 'experiment' due to our emission of greenhouse gases,” Marchitto says. “To predict the outcomes of that experiment we need a better understanding of how Earth's climate behaves when its energy balance is altered. The new AI, and the robotic system it will enable, could significantly expedite our ability to learn more about the relationship between the climate and the oceans across vast time scales.”
The paper, “Automated species-level identification of planktic foraminifera using convolutional neural networks, with comparison to human performance,” is published in the journal Marine Micropaleontology.
Lead author of the paper is Ritayan Mitra, a former postdoctoral researcher at NC State and the University of Colorado Boulder, who is now at IIT Bombay. Co-authors include Q. Ge and B. Zhong, Ph.D. students at NC State; B. Kanakiya, a former master's student at NC State; M.S. Cook of Williams College; J.S. Fehrenbacher of Oregon State University; J.D. Ortiz of Kent State University; and A. Tripati of UCLA.
The AI work was done with support from NSF under grant number 1637039.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



