First successful exchange of quantum keys via optical fiber
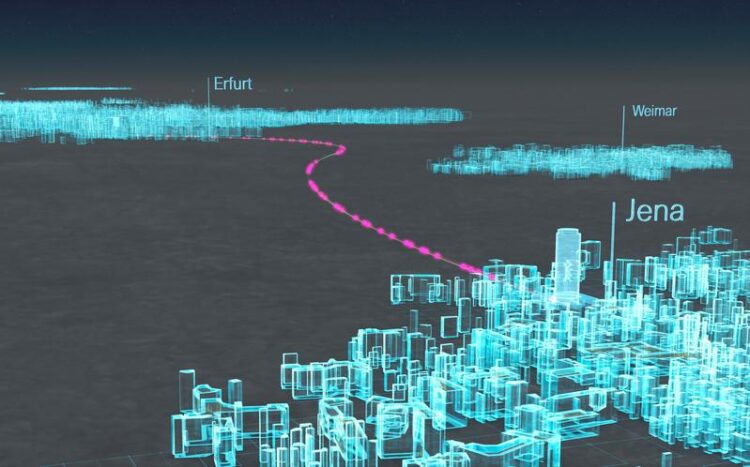
The quantum fiber link between Jena and Erfurt extends over 75 kilometers.
Credit: Christian Süß © Fraunhofer IOF
Fiber link over 75 kilometers enables new QKD experiments.
The Thuringian Ministry of Science has provided eleven million euros in funding for developing an infrastructure for quantum communication networks in the Free State Thuringia, Germany. This includes a fiber-based test route between Jena and Erfurt. Partners of the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Optics and Precision Engineering IOF have now successfully exchanged quantum keys on the 75 km route for the first time.
It is a milestone for the research of high-security quantum communications in Thuringia and Germany: on a test route between Jena and Erfurt, quantum keys have been successfully exchanged for the first time over a distance of 75 kilometers via optical fiber. More than 300,000 quantum keys were sent between the Thuringian cities over a test period of ten days.
The test route, funded by the state, had already been completed in the spring of this year. It connects Fraunhofer IOF in Jena with the Fraunhofer Center for Microelectronic and Optical Systems for Biomedicine (MEOS) in Erfurt. It has now been successfully launched with the latest test runs.
Thuringia to become a quantum hub
Thuringia’s Minister of Economics Wolfgang Tiefensee is delighted with the launch: “Thuringia is one of the leading locations in the field of quantum communication. As a state, we have been investing specifically in the expansion of these competencies for years. The test track is another important and very concrete step in this direction. It will become the starting point for a secure quantum communications infrastructure throughout Germany. Thuringia, with its research institutions and companies, will form a central hub in this.”

Credit: Walter Oppel / © Fraunhofer IOF
The special added value of the test route: it takes highly complex technologies for quantum key distribution (QKD) out of the laboratory and introduces them into a real, everyday infrastructure. Accordingly, the test route uses conventional optical fiber, for example, as it is already used today in IT infrastructures. It could thus be the basis for a nationwide implementation of quantum systems in the future. Also, about 6 kilometers of the test routes run above ground, allowing scenarios of already existing networks to be simulated.
“For quantum networks of the future, it is important to test novel systems in real infrastructures,” explains Prof. Dr. Andreas Tünnermann, director of Fraunhofer IOF. “Our test route should be explicitly accessible to partners from industry and business. As Fraunhofer IOF, we want to enable entrepreneurs to test and optimize their own systems for quantum communications in practical everyday scenarios.”
First successful quantum key exchange
The first company that has now successfully exchanged quantum keys on the fiber test route with the support of Fraunhofer IOF is Quantum Optics Jena GmbH. In 2020, the young start-up had spun off from the Fraunhofer Institute and has since been developing plug-in solutions for quantum communications. “We are really excited about the successful test run,” says Dr. Kevin Füchsel, CEO of Quantum Optics Jena. “But we are also grateful to Fraunhofer IOF for the opportunity to test our system under everyday conditions. In this way, we jointly promote a transfer of science into industry and the practical everyday life of users.”
For the colleagues from Quantum Optics Jena, the first test on the test route immediately yielded exciting results: “We see that the system works differently in the real field than in the laboratory,” Füchsel continues. “In the lab, we transmit at about 300 bits per second with comparable losses. That gives us one encryption key per second. In the field, we’re at about 200 bits, so a little less. A key is 256 bits long and can therefore be renewed almost every second for cryptographic protection, i.e., encryption and decryption, of the transmitted information. It is precisely this fast, tap-proof and automated key renewal that distinguishes quantum key distribution from established methods.”
Quantum Optics Jena is planning a second test run in the near future to further deepen the results obtained from the first test run and to develop further solutions.
Planned expansion of the line in the direction of Saxony and Bavaria
“So far, our test route offers a two-node connection between Erfurt and Jena,” says institute director Tünnermann, discussing the current locations. But there are already plans for the future: “We hope to expand our test route even further and establish a network in the direction of Saxony and Bavaria.”
The fiber route was created as part of the Thuringian Ministry of Science’s funding for quantum application laboratories. In addition to the test route, state-of-the-art laboratories for the generation as well as analysis of quantum states and their application in high-security communications were established in Erfurt and Jena. The funding from the state of Thuringia is closely coordinated with federal initiatives. It is also part of the digitalization project of the Thuringian Ministry of Economy, Science and Digital Society.
Quantum key exchange over ever greater distances
Light particles, known as quanta, are expected to make our communications highly secure in the future. This requires the creation of systems that enable a reliable exchange of so-called quantum keys over various distances.
Fraunhofer IOF has been researching various possibilities for transmitting highly secure quantum keys for some time. As part of the QuNET initiative, a pilot project of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, a free-beam link was set up between the Jena public utility company and Fraunhofer IOF on the Beutenberg campus in Jena. Quantum keys are exchanged here over a distance of 1.7 kilometers by means of free beams.
The exchange of quantum keys via fibers is now the next step to realize even larger distances. In order to be able to encrypt global communication networks in a quantum-safe manner, an exchange via satellites is also envisaged in the future.
More information:
https://www.iof.fraunhofer.de/en/pressrelease/2022/quantum-keys-exchange-success…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



