Georgia Tech discovers how mobile ads leak personal data
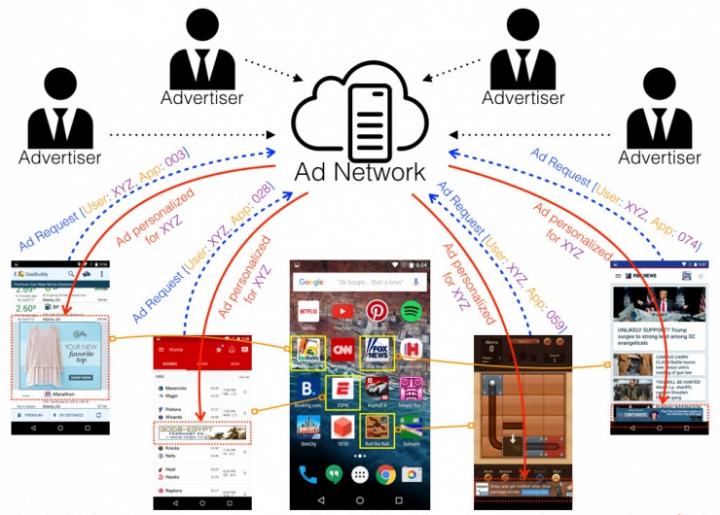
Caption Ad networks deliver personalized ads inside mobile apps, which can leak sensitive profile information about the user to the mobile app developer. Credit: Georgia Tech
The personal information of millions of smartphone users is at risk due to in-app advertising that can leak potentially sensitive user information between ad networks and mobile app developers, according to a new study by the School of Computer Science at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
Results will be presented Tuesday, Feb. 23 at the 2016 Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS '16) in San Diego, Calif., by researchers Wei Meng, Ren Ding, Simon Chung, and Steven Han under the direction of Professor Wenke Lee.
The study examined more than 200 participants who used a custom-built app for Android-based smartphones, which account for 52 percent of the U.S. smartphone market according to comScore's April 2015 report. Georgia Tech researchers reviewed the accuracy of personalized ads that were served to test subjects from the Google AdNetwork based upon their personal interests and demographic profiles; and secondly, examined how much a mobile app creator could uncover about users because of the personalized ads served to them.
Researchers found that 73 percent of ad impressions for 92 percent of users are correctly aligned with their demographic profiles. Researchers also found that, based on ads shown, a mobile app developer could learn a user's:
gender with 75 percent accuracy,
parental status with 66 percent accuracy,
age group with 54 percent accuracy, and
could also predict income, political affiliation, marital status, with higher accuracy than random guesses.
Some personal information is deemed so sensitive that Google explicitly states those factors are not used for personalization, yet the study found that app developers still can discover this information due to leakage between ad networks and app developers.
“Free smart phone apps are not really free,” says Wei Meng, lead researcher and a graduate student studying computer science. “Apps – especially malicious apps – can be used to collect potentially sensitive information about someone simply by hosting ads in the app and observing what is received by a user. Mobile, personalized in-app ads absolutely present a new privacy threat.”
How it Works
-Mobile app developers choose to accept in-app ads inside their app.
-Ad networks pay a fee to app developers in order to show ads and monitor user activity – collecting app lists, device models, geo-locations, etc. This aggregate information is made available to help advertisers choose where to place ads.
-Advertisers instruct an ad network to show their ads based on topic targeting (such as “Autos & Vehicles”), interest targeting (such as user usage patterns and previous click thrus), and demographic targeting (such as estimated age range).
-The ad network displays ads to appropriate mobile app users and receives payment from advertisers for successful views or click thrus by the recipient of the ad.
-In-app ads are displayed unencrypted as part of the app's graphical user interface. Therefore, mobile app developers can access the targeted ad content delivered to its own app users and then reverse engineer that data to construct a profile of their app customer.
Unlike advertising on a website page, where personalized ad content is protected from publishers and other third parties by the Same Origin Policy, there is no isolation of personalized ad content from the mobile app developer.
For the smartphone dependent population – the 7 percent of largely low-income Americans, defined by Pew Internet (“U.S. Smartphone Use in 2015”), who have neither traditional broadband at home nor any other online alternative – their personal information may be particularly at risk.
“People use their smartphones now for online dating, banking, and social media every day,” said Wenke Lee, professor of computer science and co-director of the Institute for Information Security & Privacy at Georgia Tech. “Mobile devices are intimate to users, so safeguarding personal information from malicious parties is more important than ever.”
The study acknowledges that the online advertising industry is taking steps to protect users' information by improving the HTTPS protocol, but researchers believe the threat to user privacy is greater than HTTPS protection can provide under a mobile scenario.
The researchers contacted Google AdNetworks about their finding.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



