Predicting new quantum echoes
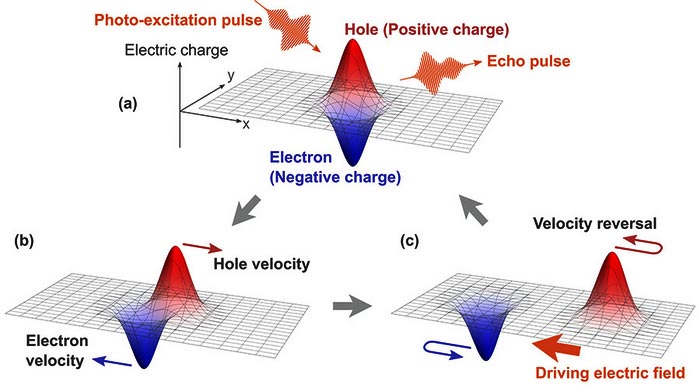
A schematic diagram of the present echo-generation process. (a) An electron-hole pair is created by a photo-excitation pulse. (b) After the excitation, the electron and hole move in opposite directions. (c) A driving electric-field pulse reverses the relative velocity of the electron-hole pairs, resulting in the recombination of the pairs and the emission of echo pulses.
Credit: Atsushi Ono
Ultrafast lightwave control of electrons in crystals.
The quantum realm of atomic particles is embedded with randomness. Still, precise control of quantum systems, such as quantum computers, is of great importance for modern quantum science and prospective quantum technology.
In the classical world, time is constantly moving forward. But in the quantum world, time is theoretically malleable and reversible. And it is through these time-reversal dynamics that scientists have attempted to control quantum systems. For example, spin echoes – proposed by Erwin Hahn in 1950 – are widely observed in quantum spin-systems and are fundamental for nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance systems.
However, the application of such time-reversal phenomenon becomes difficult in more sophisticated, quantum condensed-matter systems – i.e., quantum systems with infinite degrees of freedom. This is because quantum coherence gets lost quickly when interacting with the environment.
Now, a research group led by Atsushi Ono, assistant professor in the Department of Physics at Tohoku University, has unearthed a new type of echo phenomenon associated with the energy-band structure in crystalline solids. So-called “energy-band echoes” were discovered after the group began theoretically investigating the ultrafast dynamics of optically driven quasiparticles in crystalline solids.
Details of their findings were published in the Journal Physical Review Research on November 30, 2022.
The group’s numerical simulation and analytical expressions revealed that quasiparticles are driven coherently by an electric field pulse, and the photoexcitation process generates echoes when the quasiparticles recombine. These echo pulses carry information about the dispersion relations of quasiparticles.
Additionally, Ono and his team observed energy-band echoes even in strongly correlated systems, where free electrons are not well-defined quasiparticles on account of many-body interactions.
“Our discovery provides a different perspective of ultrafast dynamics that are driven and controlled by a lightwave,” Ono said. “Energy-band echoes could be used for all-optical momentum-resolved spectroscopy of quasiparticles in both crystalline solids and cold atoms in optical lattices, even when strong many-body correlations are present.”
Journal: Physical Review Research
Article Title: Energy-band echoes: Time-reversed light emission from optically driven quasiparticle wave packets
Article Publication Date: 30-Nov-2022
Media Contact
Public Relations
Tohoku University
public_relations@grp.tohoku.ac.jp
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



