Smart maths for greener mill design
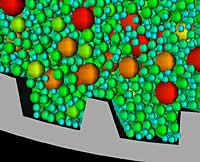
A webGF-Mill image showing the motion of particles adjacent to a lifter bar. Particle colouring indicates particle diameter; red indicating large particles and blue indicating small particles
CSIRO has developed an Internet-based simulation tool that predicts the motion of particles inside grinding mills, providing insight into the way mills work and enabling huge energy savings from smarter, more energy efficient design.
webGF-Mill assesses the design and function of the grinding mills used at mines to crush ore.
“Improving mill design is important because of the amount of energy that mills use,” says CSIRO mathematician Dave Morton. “Typically, grinding mills are very inefficient. An average mill around 10 metres in diameter consumes roughly the energy required to supply 10 000 average Australian households. Unfortunately, only 5% of this energy is consumed by the processes that actually break the rocks inside the mill.”
“As well as decreasing costs for mining companies, improving mill performance has the potential to significantly reduce global consumption of fossil fuels and thus provide important environmental benefits,” he says.
webGF-Mill, uses sophisticated simulation techniques to predict the collective motion of large numbers of particles. These methods, developed by CSIRO mathematicians, provide tools for studying the flow of granular materials such as minerals, powders and cereals. Understanding the way that granules move helps companies develop efficient methods for production, processing and transport of these materials.
webGF-Mill is used to study three types of mills, the larger SAG (semi-autogenous grinding) and AG (autogenous grinding) mills, and the smaller ball mills.
As Australia is one of the world’s largest mineral producers, many mills are used at mine sites throughout Australia.
Typically, material is dug out of a mine as rocks up to 2m in size. Crushers break the rocks down to particles of around 200-300mm, which are then ground further in a SAG or AG mill. Oversized particles are then sent to ball mills for further crushing. Crushed material accepted from SAG, AG and ball mills is sent to flotation plants where valuable minerals are separated from the dirt for further processing.
webGF-Mill can be used to simulate a variety of different mill sizes, lifter geometries, ball and rock distributions, and fill levels.
For further information visit www.cmis.csiro.au/webgf
More information:
Dave Morton, mobile: 0407 257 281
Email: dave.morton@csiro.au
CSIRO Mathematical and Information Sciences
Media assistance :
Andrea Mettenmeyer, mobile: 0415 199 434
Email: andrea.mettenmeyer@csiro.au
CSIRO Mathematical and Information Sciences
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.csiro.au/index.asp?type=mediaRelease&id=PrGFmillAll latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



