Cornell Web map enabling researchers to drill down to detailed features of Sri Lanka tsunami damage
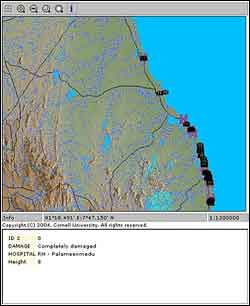
An example image from Cornell’s Sri Lanka GIS web site, showing the locations of damaged schools and hospitals on about 40 miles of the eastern coast of the island, centered on the destroyed Palameedmedu Hospital. Hospitals are indicated by the letter H, and schools by small black rectangles. This view includes only roads, natural bodies of water and flooded areas, but users can add other features as needed or click through for detailed data. Copyright © Cornell University
Kinniya Hospital on the east coast of Sri Lanka was destroyed by the Dec. 26 tsunami, and its 40 patients and hospital staff are missing. It was just one of many buildings poorly prepared for actual disaster. In the weeks and months ahead, scientists and engineers will be studying damage sites all over the island to evaluate the power of the tidal wave and recommend new construction standards to help such buildings withstand the expected stresses.
A new Web site at Cornell University is giving researchers the information they need as well as helping relief workers do their jobs on the devastated island. The creator of the site hopes it will serve as a model for the distribution of information in future disasters.
The site provides a map of the island nation on which users can display separately or together the precise locations of roads, waterways, hospitals, schools, flooded areas, displaced person’s camps, even footpaths, and zoom in, sometimes to the block level. The maps are built from Geographic Information System (GIS) databases supplemented by field observations using Global Positioning System (GPS) instruments. Included are links to photographs and videos of damaged locations, identified by their precise latitude and longitude, plus high-resolution satellite imagery of the damaged areas. Coming soon will be links to data on wave heights at various locations.
“Lots of people have put up maps on the Internet, but we’re the only ones with data down to this local level,” says Cornell senior research associate Arthur Lembo Jr., who had a preliminary version of the site up and running some four hours after the disaster. “People now can sit in their offices in Ithaca or anywhere in the world and see the kinds of data that researchers in the field are collecting.”
It was possible to get the site up and running so quickly, he says, because scientists at the International Water Resources Institute, coincidentally located in Colombo, Sri Lanka, went out immediately after the wave hit and gathered information, adding it to an already extensive GIS database and making it available on the Internet. They have continued to update the databases since then.Navigation through the site can be difficult for those not familiar with GIS systems, Lembo notes. “This is more for the people who know what they’re doing. It’s not geared for the general public,” he says. He plans to create another site with a more intuitive user interface for the nonprofessional audience.
GIS systems use a standard format for encoding information that is tied to a spatial location, which can include everything from physical features of a site to demographics. Data made available in GIS format can be used to make maps, charts and other presentations, which often combine information from a variety of sources. Users of the Cornell site can turn the various sources on and off, displaying, for example, just hospital locations, displaced persons camps and road maps to see where supplementary medical aid might be needed.
Engineers are studying the damage caused by the tsunami in order to recommend how buildings might be designed to reduce future damage and to learn how the behavior of the tsunami relates to what is known about the earthquake that launched it. Tsunami expert Philip Liu, Cornell professor of civil and environmental engineering, who has just returned from a scientific study of the Sri Lankan disaster areas, carried a GPS device and returned with a collection of digital photos identified by their precise geographic locations, which will be incorporated into the Web site. Besides showing the extent of the damage, the photos provide clues to the nature of the tsunami, such as high-water marks.
Lembo says the site also will be used by social scientists to study how well government and social agencies responded to the disaster. Knowing such things as the locations of towns, hospitals and schools in relation to areas of damage will be useful, he notes.
Currently, high-resolution satellite imagery from Space Imaging Inc. is used to illustrate areas of damage, and generalized elevation data collected during NASA’s space shuttle missions also are included. Soon to be added are even higher resolution satellite photos from Digital Globe, a company that serves the GIS community with the highest resolution satellite photos available commercially. Researchers who need satellite photos of particular areas can request them through Cornell’s site.
Lembo is using the opportunity presented by the tsunami to study how geographic data is handled in times of disaster. “We want to find out how to use the technology to get information to first responders in the first hours after a disaster,” he explains. “A key part of it is thinking about how we go out and collect data. We’re trying to back up [our GIS response] from days after an event to within a few hours.” In some cases, he says, people collect data and post them in the form of maps, but then the raw data are not available. In this case, he says, scientists in Colombo put their data on an Internet file transfer (FTP) site and posted new data each day as they gathered them. “The model we’re going to propose,” he says, “is that when you have a disaster the most important thing is making the data available so researchers can use them.” Lembo has applied similar technology to an analysis of the locations of California hospitals with respect to nearby earthquake faults. He plans further applications of Internet map server technology as a tool to be used during and after disasters, including a collaboration with the New York State Homeland Security Group.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Time to Leave Home? Revealed Insights into Brood Care of Cichlids
Shell-dwelling cichlids take intense care of their offspring, which they raise in abandoned snail shells. A team at the Max Planck Institute for Biological Intelligence used 3D-printed snail shells to…

Smart Fabrics: Innovative Comfortable Wearable Tech
Researchers have demonstrated new wearable technologies that both generate electricity from human movement and improve the comfort of the technology for the people wearing them. The work stems from an…

Going Steady—Study Reveals North Atlantic’s Gulf Stream Remains Robust
A study by the University of Bern and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in the USA concludes that the ocean circulation in the North Atlantic, which includes the Gulf Stream,…



