Tiny, cheap solution for quantum-secure encryption
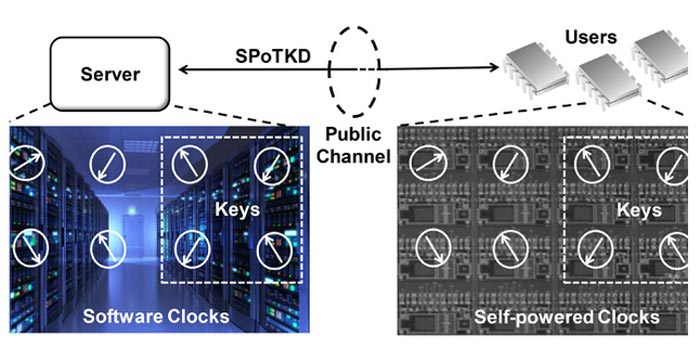
Securing a channel of communication using SPoTKD requires a server with clocks synched to those on tiny, self-powered chips.
Credit: WashU/Shantanu Chakrabartty
Microchips with tiny clocks may hold key to future of computing security.
It’s fairly reasonable to assume that an encrypted email can’t be seen by prying eyes. That’s because in order to break through most of the encryption systems we use on a day-to-day basis, unless you are the intended recipient, you’d need the answer to a mathematical problem that’s nearly impossible for a computer to solve in a reasonable amount of time.
Nearly impossible for modern-day computers, at least.
“If quantum computing becomes a reality, however, some of those problems are not hard anymore,” said Shantanu Chakrabartty, the Clifford W. Murphy Professor and vice dean for research and graduate education in the Preston M. Green Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering.
Already these new computing paradigms are becoming a reality and could soon be deployable. Hackers are already preparing by storing encrypted transactions now with the expectation they can decipher the information later.
Chakrabartty’s lab at Washington University in St. Louis proposes a security system that is not only resistant to quantum attacks, but is also inexpensive, more convenient, and scalable without the need for fancy new equipment.
This research will appear in the IEEE Transactions of Information Forensics Science. It is available now on the IEEE Xplore early access portal.
Security is often managed today by key distribution systems in which one person sends information hidden behind a key, maybe a long string of seemingly unassociated numbers. The receiver of that information can access the information if they possess another specific key. The two keys are related in a mathematical way that is nearly impossible to guess, but can be easily solved with the right algorithm or using a quantum computer.
There have been potential solutions for securing data against a “quantum attack.” Some technologies have been commercialized already. But they are computationally very expensive or require dedicated optical fibers or satellite links via lasers.
The new protocol for Symmetric Key Distribution, which Chakrabartty and Mustafizur Rahman, a PhD student in Chakrabartty’s lab and first author on the research paper, refer to as SPoTKD, doesn’t require lasers or satellites or miles of new cable. It relies on tiny microchips embedded with even tinier clocks that run without batteries.
The clocks are really electrons that seem to magically transport themselves between two locations on the chip using quantum tunneling; the “time” refers to the motion of the electrons. When the chips are created, their initial state is also recorded on a computer server.
If someone wants to create a secure channel, they note the time on a subset of the clocks and send that information to the server, which can use its knowledge of the initial state to determine what time the clocks read at the time they were sent. The server lets the person know what the times were and, if correct, a secure channel of communication has been opened.
The quantum nature of the electrons’ transport adds some extra layers of security; if they are measured, the clock collapses. It will disappear forever and neither a spy nor the recipient can access the information.
And, as Chakrabartty has shown in the past, these kinds of systems can also power themselves for extended periods of time with the slightest energy input at the outset, thanks to the properties of quantum tunneling. This is another security advantage of his SPoTKD: it doesn’t rely on outside energy to power it.
“A big vulnerability would be if you could tap into the power source,” Chakrabartty said. “You would be able to monitor the fluctuations in power consumption to get secret information.”
Chakrabartty is working on some additional features for these chips, including the ability to self-destruct after a specified period of time. A provisional US patent for the technology has been filed by the Office of Technology Management.
Ultimately, SPoTKD could be used to make sure medical records are destroyed after being read by a doctor, or to enforce time limits on software licenses. They can secure voting records or validate NFTs or just make sure no one is reading your email.
Journal: IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security
DOI: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3158089
Method of Research: Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: SPoTKD: A Protocol for Symmetric Key Distribution over Public Channels Using Self-Powered Timekeeping Devices
Article Publication Date: 8-Mar-2022
Media Contact
Brandie Jefferson
Washington University in St. Louis
brandie.jefferson@wustl.edu
Office: 314-935-5272
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



