Lipoprotein nanoplatelets shed new light on biological molecules and cells
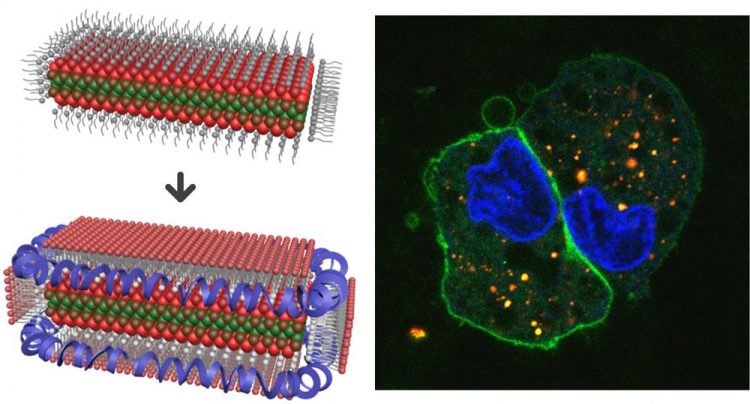
A new composite material has been made by entrapping crystalline sheets called nanoplatelets into lipoprotein nanoparticles. These lipoprotein nanoplatelets are brightly fluorescent and enter cells rapidly. Credit: Sung Jun Lim, University of Illinois
“Quantum dots are being widely investigated due to their unique physical, optical, and electronic properties,” explained Andrew M. Smith, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Illinois. “Their most important feature is bright, stable light emission that can be tuned across a broad range of colors. This has made them useful for diverse applications as imaging agents and molecular probes in cells and tissues and as light-emitting components of LEDs and TVs.”
“These studies are the first example of flat quantum dots, called nanoplatelets, in biological systems,” said Smith, whose work is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“We have developed a unique nanoparticle that is flat, like a disc, and encapsulated within a biological particle. These are derived from quantum dots and they similarly emit light, however, they have a slew of interesting optical and structural properties because of their shape.
Their light absorbing and light emitting properties are closer those of quantum wells, which are thin-layers used to make lasers. We find that these particles uniquely enter cells very rapidly and we are using them as sensors in living cells.”
“The new colloidal material is a hybrid between an inorganic quantum well and an organic nanodisc composed of phospholipids and lipoproteins,” explained Sung Jun Lim, a postdoctoral fellow in Smith's research group and first author of the paper, “Lipoprotein Nanoplatelets: Brightly Fluorescent, Zwitterionic Probes with Rapid Cellular Entry.”
“The phospholipids bind to the flat faces on the nanoplatelet and lipoproteins bind to curved edges to homogeneously entrap the particles in biocompatible materials. They have long-term stability in biological buffers and high salt solutions and are highly fluorescent, with brightness comparable to quantum dots when measured in a solution or at the single-molecule level in a microscope.”
According to Smith, these particles are especially useful for single-molecule imaging, where quantum dots have made the biggest impact due to their unique combination of high light emission rate and compact size. Quantum dots have recently enabled the discovery of a host of new biological processes related to human health and disease.
“We think the new capabilities provided by nanoplatelets are valuable for imaging biological molecules and cells, but it was previously challenging to stabilize these nanocrystals in biological media because their unusual dimensions cause them to stick together, aggregate, and lose fluorescence. This new class of nanoplatelets solves these problems and they are stable under harsh biological conditions because they are encapsulated in lipoproteins.
“We expect that this new material composite will reveal, at the single-molecule level, how flat materials interact with biological systems,” Smith added. “The unique finding of rapid cellular entry suggests that these materials may be immediately useful for cellular labeling applications to allow highly multiplexed spectral encoding of cellular identity so that we can track metastatic cancer cells in the body. Unique shapes of nanoparticles also have been found to be more efficient for delivering drugs to tumors compared with standard spherical particles, so we are exploring this as well.
###
This work is the result of a collaboration between Smith's lab and the research group of Aditi Das, an assistant professor of comparative biosciences at Illinois. Other co-authors of the research paper include Mohammad U. Zahid, Daniel R. McDougle, Liang Ma, and Aditi Das. The paper is available online: http://pubs.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Interdisciplinary Research
News and developments from the field of interdisciplinary research.
Among other topics, you can find stimulating reports and articles related to microsystems, emotions research, futures research and stratospheric research.
Newest articles

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…

ASXL1 Mutation: The Hidden Trigger Behind Blood Cancers and Inflammation
Scientists show how a mutated gene harms red and white blood cells. LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have discovered how a mutated gene kicks off…



