Nanocontainers introduced into the nucleus of living cells
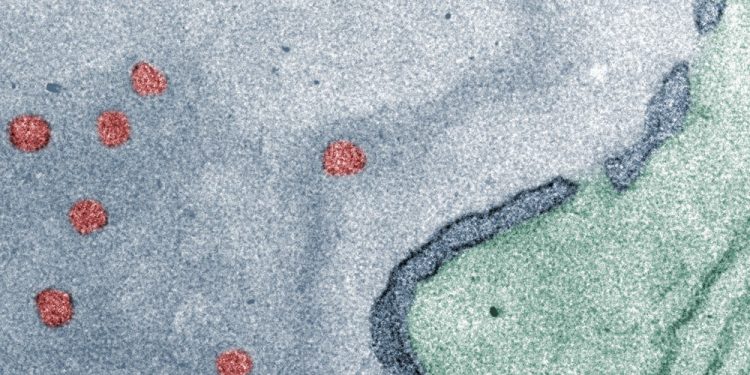
To enter into the cell nucleus (grey), the polymersomes (red) must selectively translocate across the nuclear membrane (dark blue) via the nuclear pore complexes (gaps in the membrane). (Image: Christina Zelmer, University of Basel, and Evi Bieler, Swiss Nanoscience Institute)
In order to combat diseases, different therapies strive to intervene in pathological processes that occur in the cell nucleus. Chemotherapies, for example, target biochemical reactions that are involved in the proliferation of cancer cells, while the objective of gene therapies is to insert a desired gene into the nucleus.
Therefore, a challenge in the field of nanomedicine is to develop a reliable method of introducing active substances specifically into the cell nucleus.
Researchers at the University of Basel have now developed tiny nanocontainers that do just that in living cells. These nanocontainers can pass through the nuclear pore complexes that control the transport of molecules into and out of the cell nucleus.
The development of these so-called polymersomes involved a highly interdisciplinary team of scientists from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute, the Biozentrum and the Department of Chemistry.
Entry ticket into the nucleus
Researchers used a trick to direct the artificial nanocontainers through the nuclear pore complexes: “These polymersomes, which are about 60 nanometers in size, are encapsulated by a flexible polymer membrane that mimics natural membranes,” explains chemist Professor Cornelia Palivan. “However, they are more robust than lipid vesicles and can be functionalized as needed.”
In addition, the researchers constructed the polymersomes with nuclear localization signals bound to them – giving them an entry ticket into the nucleus, so to speak. Cells use these signals to differentiate between molecules that need to be transported into the nucleus and those that should be kept out. In this way, the nuclear localization signals are used to disguise the artificial nanocontainers as permissible cargo.
Inspired by nature
“The presence of nuclear localization signals enables the polymersomes to hijack the cellular transport machinery that delivers cargo through the nuclear pore complexes,” explains Professor Roderick Lim. This property is similarly based on nature: “This strategy is also used by some viruses,” said the biophysicist.
The researchers were able to track the path of the polymersomes into the cell nucleus by filling them with different dyes and observing them using various microscopic techniques. This confirmed the successful transport of the artificial nanocontainers into the cell nucleus in vitro as well as in vivo within living cells. For future investigations, these dyes will be replaced by therapeutic agents.
“These findings show that the polymersomes we have developed make it possible to deliver artificial cargo very specifically into the cell nucleus. Indeed, nanocontainers without nuclear localization signals could not be detected in the cell nucleus,” according to first author Christina Zelmer, summarizing the study.
Prof. Dr. Roderick Lim, University of Basel, Biozentrum and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute, tel. +41 61 207 20 83, email: roderick.lim@unibas.ch
Prof. Dr. Cornelia G. Palivan, University of Basel, Department of Chemistry, tel. +41 61 207 38 39, email: cornelia.palivan@unibas.ch
Christina Zelmer, Ludovit P. Zweifel, Larisa E. Kapinos, Ioana Craciun, Zekiye P. Güven, Cornelia G. Palivan and Roderick Y.H. Lim
Organelle-specific targeting of polymersomes into the cell nucleus
PNAS (2020), doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916395117
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1916395117
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Interdisciplinary Research
News and developments from the field of interdisciplinary research.
Among other topics, you can find stimulating reports and articles related to microsystems, emotions research, futures research and stratospheric research.
Newest articles

Self-Destructing Cancer Cells: Cutting-Edge RNA Breakthrough
Jülich scientists use novel RNA technology to selectively switch off tumours in the brain. An Adaptable Platform Technology That Destroys Glioblastoma Cancer Cells Using a special RNA molecule, a team…

Endurance Training: Transforming Lives of Heart Failure Patients
Can strength and endurance training be beneficial for patients with a certain form of heart failure? A research team from Greifswald investigated this question together with seven other research centers…

A Wake-Up Call for Mediterranean Shark Protection Against Extinction
Overfishing, illegal fishing and increasing marketing of shark meat pose significant threats to the more than 80 species of sharks and rays that inhabit the Mediterranean Sea, according to a…



