A new species of deep-sea fish discovered in the Atacama Trench
Paraliparis selti
Credit: Dr Thom Linley
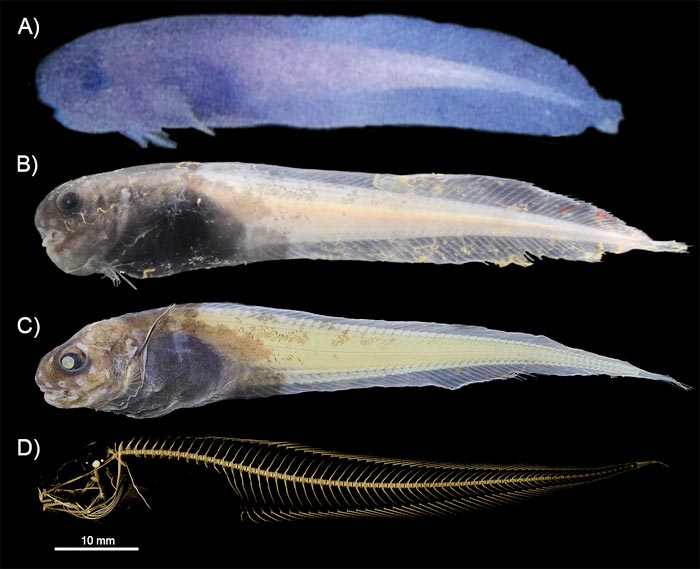
A new small blue snailfish is changing our understanding of the world’s deepest fishes.
In 2018, an international team of scientists studied the Atacama Trench, an expansive trench that runs along the west coast of South America as a deep underwater valley that mirrors the Andes Mountains. The team, including Newcastle University scientists, deployed free-falling landers to sample the sparse deep-sea creatures around cameras and traps with bait. Two lander systems from Newcastle University recorded three types of hadal snailfish and one of them was not like the others.
The small blue fish, seen from about 6,000 to 7,600 m deep, doesn’t look like other hadal snailfish. With large eyes and striking colour, it resembles other species of snailfishes that are found living in much shallower waters. The team used a 3D x-ray technique called microcomputed tomography (micro-CT) and DNA barcoding to see where the new species fit within the snailfish family.
To the team’s surprise, the new species appears to be a separate coloniser of the Atacama Trench. The new species belongs is a member of the genus Paraliparis. Species in this genus are particularly abundant in the Southern Ocean of the Antarctic and are rarely found deeper than 2,000 m. Significantly, this is the first time this genus has been found living in the hadal zone.
The team named the new species Paraliparis selti, meaning blue in the Kunza language of the indigenous peoples of the Atacama Desert. The description is published in the journal Marine Biodiversity.
Study lead author, Dr Thom Linley, a visiting researcher at Newcastle University said: “I find this family of fishes absolutely fascinating. They are not at all what we expect from a deep-sea fish and I love to show people that the world’s deepest fishes are actually pretty cute.
“For me to get a camera down to where these animals live, it’s made of inches thick stainless steel and sapphire glass. It then films these delicate and beautiful animals perfectly adapted to this extreme environment. With engineering-built force we can only clumsily visit these animals for a short time.
“We have been wondering for some time just what makes this type of fish so good at living deep. Maybe it was a series of lucky accidents, a chance fluke, that happened in one lineage. Finding this new species tells us that it’s bigger than that. Lightning struck twice and there is something special about this Family.
“Paraliparis selti provides a fantastic opportunity to explore what allows fish to live so deep. If we only had a single lineage to study, we could never be sure which traits were just part of that lineage and which are the deep-sea secret sauce.”
The new species may have evolved from the cold-adapted species of the Southern Ocean. This little blue fish opens new questions about the relationship between cold temperature and high-pressure adaptation and gives a new understanding of how and when life went deep.
Reference
Linley TD, Gerringer ME, Ritchie H, Weston JNJ, Scott-Murray A, Fernandez V, Canto-Hernández J, Wenzhöfer F, Glud RN, Jamieson AJ (2022) Independent radiation of snailfishes into the hadal zone confirmed by Paraliparis selti sp. nov. (Perciformes: Liparidae) from the Atacama Trench, SE Pacific. Marine Biodiversity. 52, 56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-022-01294-0
Journal: Marine Biodiversity
DOI: 10.1007/s12526-022-01294-0
Method of Research: Observational study
Subject of Research: Animals
Article Title: Independent radiation of snailfishes into the hadal zone confirmed by Paraliparis selti sp. nov. (Perciformes: Liparidae) from the Atacama Trench, SE Pacific
Article Publication Date: 1-Oct-2022
Media Contact
Ivan Lazarov
Newcastle University
ivan.lazarov@ncl.ac.uk
Office: 07-927-369-951
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



