AI helps to spot single diseased cells
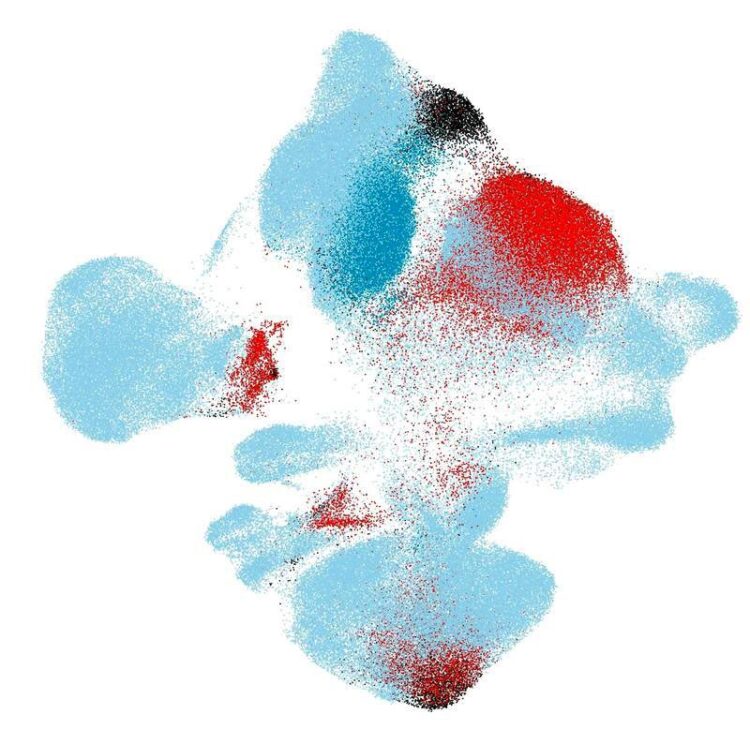
Mapping new cohorts of cells of healthy individuals and COVID-19 patients onto a healthy cells reference atlas
Credit: Helmholtz Zentrum München / Mohammad Lotfollahi
The Human Cell Atlas is the world’s largest, growing single-cell reference atlas. It contains references of millions of cells across tissues, organs and developmental stages. These references help physicians to understand the influences of aging, environment and disease on a cell – and ultimately diagnose and treat patients better. Yet, reference atlases do not come without challenges. Single-cell datasets may contain measurement errors (batch effect), the global availability of computational resources is limited and the sharing of raw data is often legally restricted.
Researchers from Helmholtz Zentrum München and the Technical University of Munich (TUM) developed a novel algorithm called “scArches”, short for single-cell architecture surgery. The biggest advantage: “Instead of sharing raw data between clinics or research centers, the algorithm uses transfer learning to compare new datasets from single-cell genomics with existing references and thus preserves privacy and anonymity. This also makes annotating and interpreting of new data sets very easy and democratizes the usage of single-cell reference atlases dramatically,” says Mohammad Lotfollahi, the leading scientist of the algorithm.
Example COVID-19
The researchers applied scArches to study COVID-19 in several lung bronchial samples. They compared the cells of COVID-19 patients to healthy references using single-cell transcriptomics. The algorithm was able to separate diseased cells from the references and thus enabled the user to pinpoint the cells in need for treatment, for both mild and severe COVID-19 cases. Biological variation between patients did not affect the quality of the mapping process.
Fabian Theis: “Our vision is that in the future we will use cell references as easily as we nowadays do for genome references. In other word, if you want to bake a cake, you usually do not want to try coming up with your own recipe – instead you just look one up in a cookbook. With scArches, we formalize and simplify this lookup process.”
Learn more about scArches: https://github.com/theislab/scarches
About the people
Computational biologist Mohammad Lotfollahi is a team leader at Fabian Theis’ lab at Helmholtz Zentrum München and doctoral student at TUM School of Life Sciences at the Technical University of Munich. He works closely with Fabian Theis, who is Director of the Institute of Computational Biology at Helmholtz Zentrum München and Coordinator of the Helmholtz Artificial Intelligence Cooperation Unit (Helmholtz AI). Theis holds the chair for Mathematical Modelling of Biological Systems at TUM.
Original publication
Lotfollahi et al, 2021: Mapping single-cell data to reference atlases by transfer learning. Nature Biotechnology, DOI: 10.1038/s41587-021-01001-7
Helmholtz Zentrum München
Helmholtz Zentrum München is a research center with the mission to discover personalized medical solutions for the prevention and therapy of environmentally-induced diseases and promote a healthier society in a rapidly changing world. It investigates major diseases which develop from the interaction of lifestyle, environmental factors and personal genetic background, focusing particularly on diabetes mellitus, allergies and chronic lung diseases. Helmholtz Zentrum München is headquartered in Neuherberg in the north of Munich and has about 2,500 staff members. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany with more than 43,000 employees at 18 research centers.
Journal: Nature Biotechnology
DOI: 10.1038/s41587-021-01001-7
Article Title: Mapping single-cell data to reference atlases by transfer learning
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



