Bacteria: Third RNA binding protein identified
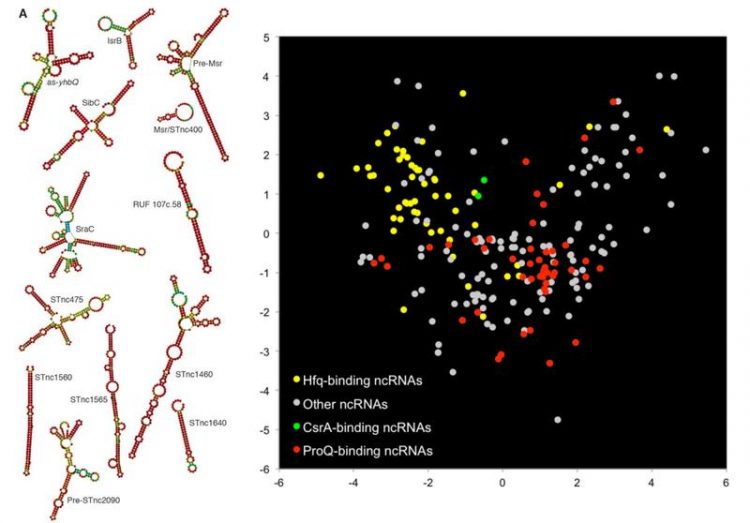
The structures of the different regulatory RNA molecules are shown left, their preferred protein binding partners on the right. (Picture: Alexandre Smirnov)
Professor Jörg Vogel, head of the Institute for Molecular Infection Biology of the Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Bavaria, Germany, is a pioneer in researching small regulatory RNA molecules. He and his team are determined to get to the bottom of how these molecules work and act. His works could also show new ways to fight pathogens.
ProQ binds nearly 100 regulatory RNAs
New findings from Vogel's team have now been published in the journal PNAS: So far, two proteins (Hfg and CsrA) have been known to bind closely to the bacteria's regulatory RNA molecules and influence their activities. Using a new self-designed method, the Würzburg team has now discovered a long-suspected third protein (ProQ) whose function inside the cell has been unknown until recently.
Experiments showed that the ProQ protein binds to 98 regulatory RNAs of the enterobacterial Salmonella enterica. The bacterium has been found to have around 300 such RNAs in total. Moreover, ProQ seems to have specialised in RNA molecules with a rather complex structure.
This protein and the RNA molecules that bind to it represent a largely unresearched class of gene activity regulators in the bacterial “RNA universe”. “It will be particularly exciting to find out how ProQ is able to pinpoint the highly structured RNAs among millions of other RNA molecules in a cell,” says Jörg Vogel.
PNAS considers results significant
These results have been reported in PNAS by the Würzburg professor together with Alexandre Smirnov, Konrad Förstner, Erik Holmqvist and Regina Günster as well as colleagues from Greifswald and Cologne. Considered highly significant for bacterial research, the new findings are featured in the journal's “Research Highlight” section.
A new technique developed by the JMU team has successfully tracked down the activities of the ProQ protein. “The methods available so far were subject to certain limits with regard to detecting and generally classifying RNA protein interactions which we have overcome here,” Professor Vogel further. Since the new method can basically be applied to any other organism, it is expected to provide more progress in researching regulatory RNA.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



