Bayreuth physicists discover mechanism for the formation of blood platelets
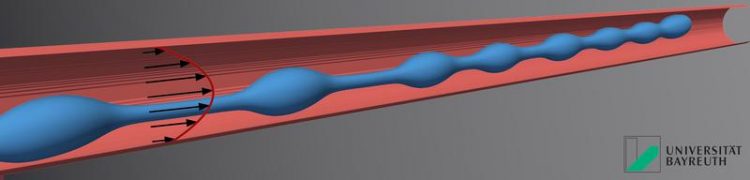
Individual droplets are formed from an elongated finger-shaped cell (blue) in the blood flow. Each droplet develops into a blood platelet. Image: UBT / Christian Bächer
Blood platelets, also called thrombocytes, are all-important cells with a diameter of between only 0.0015 and 0.003 millimetres. They have the task of resealing injuries to the blood vessels as quickly as possible, for which they constantly patrol the bloodstream, ready to react immediately to any leaks.
However, the biological capabilities of the organism alone are not sufficient to ensure that the immense number of platelets required for this is available at all times. Indeed, it takes the support of a particularly efficient physical mechanism.
This mechanism has now been discovered and scientifically described by a Bayreuth research team led by Prof. Dr. Stephan Gekle, together with partners at University Hospital Würzburg.
The platelets are formed in the blood vessels by special cells that are localised in the bone marrow, and from which thin finger-like structures extend into the bloodstream.
From there, it is rather similar to a water tap: just as a thin stream of water disintegrates into individual droplets due to surface tension, these finger-like structures break up into individual droplets. From each of these droplets one new platelet is formed.
“With computer simulations, it is possible to follow these processes in detail and to visualize them. This basic research promises to be of great practical value to medicine – especially when it comes to optimizing bioreactors currently used in the artificial production of thrombocytes,” says Gekle, who holds a Lichtenberg professorship for the simulation and modelling of biofluids at the University of Bayreuth.
The interest in biological-medical questions, combined with large-scale computer simulation, has a long tradition in physics at the University of Bayreuth.
Ever since his bachelor studies, Christian Bächer, doctoral researcher and graduate of the Bayreuth study programme “Biological Physics”, and first author of the study published in PNAS, has been fascinated by how modern IT technology brings together physical and biological research.
“It is always fascinating how processes in living beings, that seem so incredibly complicated at first glance, can often be understood on the basis of simple physical principles,” says Bächer.
Research funding:
The research work at the University of Bayreuth was funded by the Volkswagen Foundation, DFG (the German Research Foundation), the Elite Network of Bavaria, and the German Academic Scholarship Foundation.
Video sequence:
https://mms.uni-bayreuth.de/Panopto/Pages/Viewer.aspx?id=3e988abe-d998-41c2-938e…
Professor Dr. Stephan Gekle
Theoretical Physics VI
University of Bayreuth
Phone +49 (0)921 / 55-4462
E-Mail: stephan.gekle@uni-bayreuth.de
Christian Bächer, Markus Bender, Stephan Gekle: Flow-accelerated platelet biogenesis is due to an elasto-hydrodynamic instability. PNAS 2020, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2002985117
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-bayreuth.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



