Biophysicists reveal secret language of bones
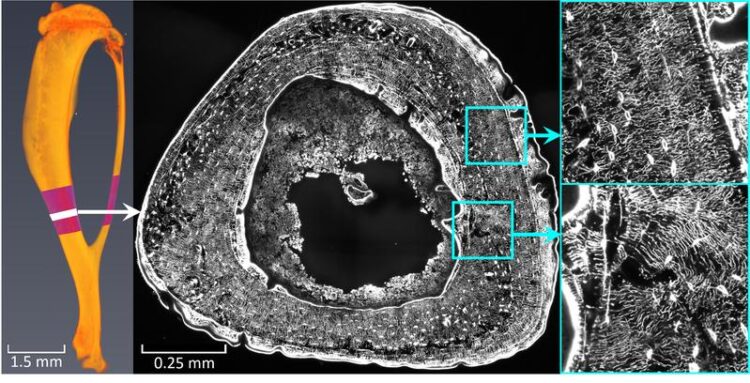
Mouse bone: Bone section under laser scanning microscope - enlarged image of the dense network architecture and the fluid flow.
Alexander van Tol / Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces
Our bones have so-called mechanosensors that react to pressure and communicate with each other. “These sensors enable that bone is formed where it is mechanically necessary and broken down elsewhere,” says Richard Weinkamer from the Biomaterials Department. In their research they have come a decisive step closer to solving the mystery of where these mechanosensors are located: Hidden within a structure of canals inside the bone, a cell network “senses” external bone stress.
This works by translating the mechanical loading into a fluid flow through this fine canal network. There are similarities between the examined network and the neural network in the brain. It may be possible to draw conclusions about diseases such as osteoporosis or arthrosis, where the network has a modified architecture.
Bones can be trained like muscles. In the course of the study, researchers in Montreal examined mouse bones that had undergone controlled “bone training”. In Potsdam, Weinkamer and his team used a scanning laser microscope to obtain 3D images of the cell network in the trained bones. The image data was used to analyze and evaluate networks with millions of canals by means of computer simulations that calculate the fluid flow through the network: “Based on our results, we are convinced that the bone cells within the networks can perceive the fluid flow, communicate with each other and thus pass on information such as ‘need of bone growth’ to other cells,” says Alexander van Tol.
He adds: “The examined mice reacted differently to bone training. A mouse that produced particularly little new bone has a network whose architecture allows only a slow flow of fluid”. He adds: “We therefore believe that the same applies to humans: Bone can be strengthened particularly well through physical activity if the network structure within the bone ‘plays along’. This study was the first to not only analyze the network architecture, but also to evaluate the quality of this architecture in terms of the perception of mechanical stimuli.
Participating scientists
Since 2003 Dr. Richard Weinkamer has been working as a biophysicist and materials researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces. He heads a five-member research group in the Biomaterials Department. His research areas include mechanobiological systems such as bones and computer modeling of growth, mechanics and adaptation of biomaterials.
Dr. Alexander Franciscus van Tol is a researcher in the biomaterials department in the group of Richard Weinkamer and first-authored the scientific study. He studied medical physics and successfully defended his dissertation on the importance of network architectures in bone in early November this year.
Press contact:
Juliane Jury
T +49 331 567 9309
M +49 170 65 10 103
juliane.jury@mpigk.mpg.de
https://www.mpikg.mpg.de/press-releases
Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces
Am Mühlenberg 1a
14476 Potsdam
Germany
Originalpublikation:
https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/12/02/2011504117#page
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



