Biosensor measures signaling molecules within cilia
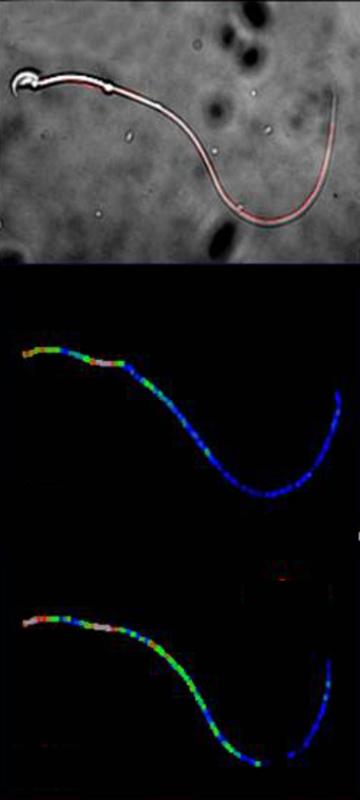
The novel biosensor within the flagellum of mouse sperm. Above: a light microscopy image of a mouse sperm. The middle image displays a normal and the lower image an increased cAMP concentration. caesar
Cells can change the way they grow, move, or develop in response to stimuli from their environment. This information is first detected at the surface of the cell and then translated into an intracellular response by signaling molecules known as “second messengers”. A molecule called cAMP is a well-known second messenger that is involved in many different signaling pathways.
Some cells have hair-like structures called cilia or flagella on their surface, which have been proposed to function as antennae for extracellular stimuli. Cilia are membrane protrusions that come in two different flavors – they can be motile or immotile. A special case of a motile cilium is the flagellum with the most prominent example being the sperm flagellum.
The second messenger cAMP plays an essential role in making motile cilia move, but it is challenging to analyze, how the levels of this molecule change over time in these structures. The levels of cAMP in live cells can only be measured using fluorescent biosensors.
Introducing these biosensors into subcellular compartments is difficult and so far, the sensors have not been sensitive enough to respond to low levels of cAMP. Furthermore, it is difficult to measure cAMP activity inside such tiny structures using these biosensors.
The team of scientists created a new cAMP biosensor that has several unique features. The sensor is based on FRET (Förster resonance energy transfer) technology. FRET is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules.
In the new created biosensor, the amount of energy tranfer depends on the distance and orientation between two light-sensitive molecules. Upon binding to cAMP, a structural rearrangement increases the distance of the two molecules and thereby decreases the amount of energy transferred between them.
Most importantly, the sensor can respond to very low levels of cAMP, making it more sensitive than previous biosensors. The caesar scientists tested this new biosensor in the flagella of sperm cells from mice, which revealed how the production of cAMP is regulated in the flagellum. The new biosensor also showed that different parts of the flagellum can have different cAMP dynamics.
In the future, this new biosensor could be used to study cAMP in other structures and compartments within cells.
Original publication
Mukherjee, S., Jansen, V., Jikeli ,J. F., Hamzeh, H., Alvarez, L., Dombrowski, M., Balbach, M., Strünker, T., Seifert, R., Kaupp U. B. & Wachten, D. (2016) “A novel biosensor to study cAMP dynamics in cilia and flagella”, eLife, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.14052
Contact
Dr. Dagmar Wachten
Minerva Max-Planck-Forschungsgruppe “Molekulare Physiologie”
Telefon: +49(0)228/9656-311
E-mail: dagmar.wachten@caesar.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.caesar.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



