Blocking the iron transport could stop tuberculosis
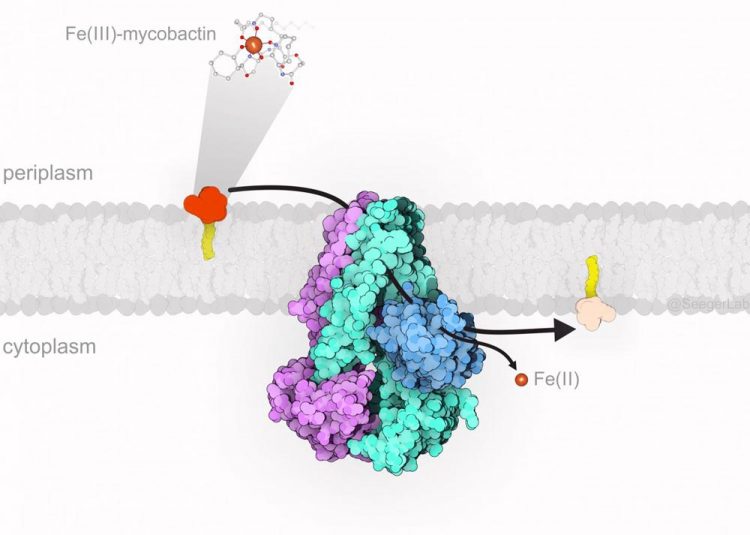
IrtAB (purple/turquoise/blue) sits in the inner membrane of M. tuberculosis and imports iron-loaded mycobactin (yellow/orange) from the host cell into the bacterial cell, where iron is released. Credit: Imre Gonda, University of Zurich
The rise of multidrug resistant M. tuberculosis strains, which are resistant to many of the most effective anti-tuberculosis drugs, is particularly worrying. In other words, novel drugs to treat tuberculosis are urgently needed.
Tuberculosis bacteria need iron to survive
All living organisms, including pathogens, need iron to survive. When a human cell is infected by pathogens like M. tuberculosis, it reduces the iron concentration to a minimum and thereby tries to starve the invader.
The tuberculosis bacteria, in turn, start to release small molecules called mycobactins. These can bind free iron extremely well and thus steel it from the host cell. The iron captured by mycobactin is then transported into the bacteria by a protein named IrtAB.
A team of researchers led by Markus Seeger, professor at the Institute of Medical Microbiology of the University of Zurich (UZH), has now analyzed in detail the protein responsible for transporting iron from the infected host cell into the bacteria.
“The transport protein, which is located in the bacterial membrane, is essential for the survival of the pathogens. If IrtAB is absent or not functioning, M. tuberculosis can no longer reproduce inside the human cell”, says Seeger.
Iron transport protein works in the opposite direction
Using a combination of cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography, the researchers solved for the first time a high-resolution structure of the transport protein IrtAB. This analysis was done in collaboration with Ohad Medalia, professor at the Department of Biochemistry of UZH.
According to its spatial structure, IrtAB belongs to the so-called ABC exporters, which are typically involved in the efflux of molecules out of the bacterial cell.
“However, we were able to show that IrtAB in fact imports mycobactins into M. tuberculosis. It therefore transports molecules in the opposite direction than expected,” says Markus Seeger.
Together with scientists from the University of Texas, USA, the research team identified an additional peculiarity of the transport protein IrtAB:
It can modify the iron bound to mycobactin after it is imported into the bacteria. The iron is thus released inside the cell and the empty mycobactin can be recycled.
Inhibiting the iron transport could lead to new tuberculosis drugs
“IrtAB is a potential drug target, because its deletion renders M. tuberculosis inactive and incapable of infection. With our structural and functional elucidation of IrtAB, we opened avenues to develop novel tuberculosis drugs that inhibit the iron transport into the bacteria”, Seeger concludes.
“In view of Covid-19, a disease that also affects the lungs, tuberculosis will likely play a more important role again in the future. It is quite conceivable that patients weakened by Covid-19 will show increased infection rates with tuberculosis,” he adds.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



