Breaking the coupling process
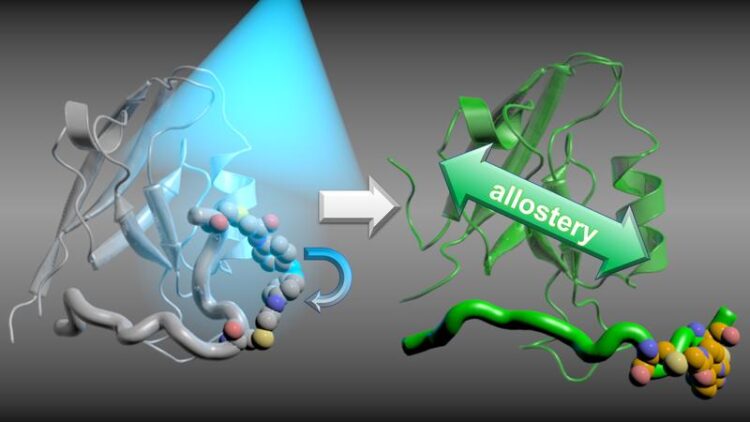
Informationen der Proteine: Eine Unterbrechung in diese Kopplung, der Allosterie, führt dazu, dass Signale nicht weitergeleitet werden.
Abbildung: Gerhard Stock, Steffen Wolf
Real-time observation of signal transmission in proteins provides new insights for drug research.
Proteins transduce information and signals within the human body by changes in their structures. For example, hormones binding to their target proteins cause a structural change which in turn opens new binding sites for other proteins elsewhere on the surface of the protein. Researchers refer to this coupling of different, distant binding sites as allostery. An interruption of this coupling leads to signals not being passed on.
This can be achieved by molecules specifically designed for this purpose, which thereby obtain pharmacological effects as analgesics or chemotherapeutic agents. To selectively design such molecules, scientists need to learn more about the possible mechanisms of allostery.
A team led by Prof. Dr. Gerhard Stock from the Biomolecular Dynamics group at the Institute of Physics at the University of Freiburg and Prof. Dr. Peter Hamm from the Institute of Chemistry at the University of Zurich, Switzerland provides important insights into the molecular details of allostery in the journal PNAS.
The researchers tracked time-resolved allosteric changes in the test protein PDZ2, which are caused by the binding of a peptide ligand. To this end, the research group at the University of Zurich performed time-resolved vibrational spectroscopy, while the physicists at the University of Freiburg simulated the corresponding changes on an atomistic level using the bwHPC cluster BinAC at Tübingen.
This combination enabled the scientists to understand how a change in the ligand binding mode induces protein structure changes passing through the protein with atomic resolution and a time scale range from picoseconds to microseconds.
The real-time observation of signal transduction in proteins showed that allostery is based on changes in both the structure and dynamics of the protein, which exhibits hierarchical dynamics, where a structural change takes about ten times longer than a preceding change.
Original publication:
Bozovic, O., Zanobini, C., Gulzar, A., Jankovic, B., Buhrke, D., Post, M., Wolf, S., Stock, G., Hamm, P. (2020): Real-time observation of ligand-induced allosteric transitions in a PDZ domain. In: PNAS. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2012999117
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Gerhard Stock
Institute of Physics
Faculty for Mathematics and Physics
University of Freiburg
Tel.: 0761/203-5750
gerhard.stock@physik.uni-freiburg.de
Originalpublikation:
https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/10/02/2012999117
https://www.pr.uni-freiburg.de/pm-en/press-releases-2020/breaking-the-coupling-process
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



