Catalysts: Poisoned and very much alive at the same time
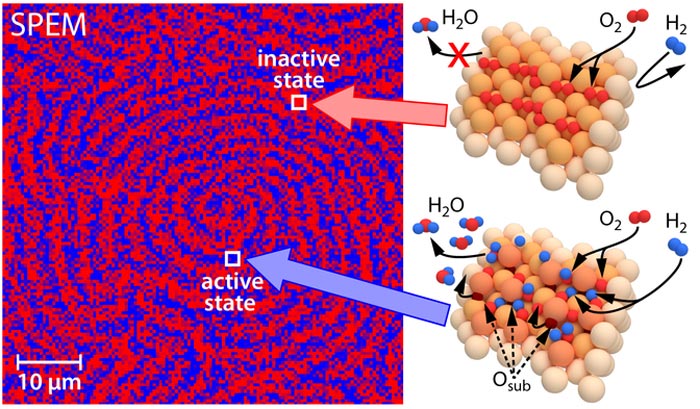
Local pattern formation in oscillatory hydrogen oxidation on rhodium: a scanning photoelectron microscope (SPEM) was used to create a chemical map of the species on the catalyst surface (left). Spectroscopic data (XPS) of the surface coverage enable to develop atomic models of the associated surface activity states (right).
Credit: TU Wien
A surprising discovery at TU Wien: A catalyst seems to contradict usual laws and can exhibit completely different activity states at the same time.
Sometimes chemical reactions in the lab work the way you imagine them to, and sometimes they don’t. Neither is unusual. What is highly unusual, however, is what a research team at TU Wien has now observed when studying hydrogen oxidation on a rhodium catalyst: The surface of a rhodium foil can be highly chemically active in some surface regions, while in others, only a few micrometers away, it is completely inactive, and still in others oscillations between the active and inactive state occur. Such behavior was previously thought to be almost inconceivable. The results, which have now been published in the scientific journal Nature Communications, show: Catalysis is more complicated than previously thought.
Basic principle of the fuel cell
“With the help of catalysts such as metallic rhodium, hydrogen can be oxidized – this is the basic reaction in fuel cells, with only water being produced as “waste gas”, says Prof. Yuri Suchorski from the Institute of Materials Chemistry at TU Vienna. Hydrogen molecules are held on the rhodium surface and split into individual atoms, which then combine with oxygen to form water.
However, it can happen that a layer of oxygen fully covers the rhodium surface, so that the hydrogen can no longer reach the rhodium atoms at all. “In this case, the surface of the catalyst is said to be poisoned,” explains Prof. Günther Rupprechter, the head of the research project. “The catalyst can no longer fulfill its function, the reaction comes to a standstill”.
Whether the catalyst does its job or is poisoned depends on external parameters, such as reactants pressures and temperature. But the rhodium foil exhibits a strange behavior in the experiment: although all areas of the surface are exposed to the same external conditions: some areas can be catalytically active, others poisoned and completely inactive, and still others switch back and forth between an active and an inactive state with different frequencies. “This sounds so unusual that until now we couldn’t even imagine that such a thing was possible,” says Philipp Winkler, the first author of the study.
Closer investigations, which the TU Vienna team conducted at the Elettra Synchrotron in Trieste together with Italian colleagues, were able to explain the observations: the polycrystalline rhodium surface is composed of different grains arranged at different angles. This means that the arrangement of atoms on the surface differs from grain to grain.
“The dynamics of the chemical reaction is surprisingly sensitive to the orientation of the grains and thus to the atomic structure of the surface,” says Yuri Suchorski. “In case of rhodium, the differences between the catalytic properties of individual structures are much larger than expected, and so it is possible for different grains to behave completely differently at the same time and under the same conditions. Here, the oscillatory behavior is particularly interesting”.
Rabbits and foxes
Similar processes are known from very different areas of science – for example, from predator-prey models: If many rabbits are born, the foxes have plenty to eat, then the next year more hungry foxes are born and the number of rabbits decreases. Just as with rabbits and foxes, the interaction of hydrogen and oxygen is a system that is in dynamic equilibrium or can oscillate between different states. Even if the populations of rabbits and foxes are initially the same everywhere, quite different temporal developments may occur in different places – for example, because rabbits are better able to hide from foxes in certain places than elsewhere. Similarly, the different chemical dynamics arise on different grains of the rhodium surface.
These results provide an important insight that has great significance for catalysis research as a whole: it is not enough to describe a catalyst globally; one must take into account its local microscopic structure and reckon with the fact that it can exhibit quite different behavior at different sites. “We are sure that such effects are significant for many different catalysts and reactions,” says Günther Rupprechter “In any case, there is still a lot to do in this field of research.”
Journal: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20377-9
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: How the anisotropy of surface oxide formation influences the transient activity of a surface reaction
Article Publication Date: 11-Nov-2021
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



