Cell Death: How a Protein Drives Immune Cells to Suicide
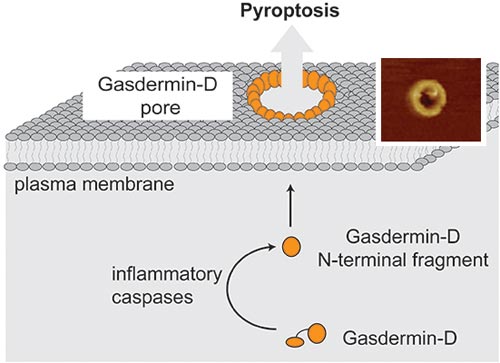
Mechanism of pore formation by the protein gasdermin D, resulting in cell death. University of Basel, Biozentrum
The best hiding place often lies behind enemy lines, as many bacteria such as the pathogens responsible for tuberculosis or typhoid have realized. They invade immune cells and can survive there, well hidden, for some time. To eliminate such invaders, the host macrophages can initiate a suicide program.
Together with researchers at the Novartis Institute for Biomedical Research and ETH Zurich, the team led by Prof. Sebastian Hiller from the Biozentrum at the University of Basel has shown for the first time that a “death protein” perforates the cell membrane, resulting in macrophage bursting open. The re-exposed pathogens can then again be fought by the immune system.
Gasdermin D: Executioner in the cell
Tiny cell components of invading pathogens are recognized by receptors inside macrophages. These, in turn, activate a signaling cascade, which triggers an inflammatory response and initiates pyroptosis – a specific form of programmed cell death.
“Some studies have already demonstrated that the protein gasdermin D plays a central role in pyroptosis,” explains Prof. Petr Broz, one of the main authors of the study. “We have now discovered how gasdermin drives immune cells to suicide and using cryo-electron and atomic force microscopy we could visualize the pores in the cell membrane.”
The protein gasdermin D is at the end of a long signaling pathway. Intracellular receptors recognizing foreign bacterial components induce the assembly of the inflammasome. This protein complex, in turn, activates enzymes that generate active gasdermin fragments by proteolytic cleavage.
“In the macrophages, gasdermin D is the executioner, which carries out the death sentence,” says Hiller, clarifying the role of the protein. “The cleaved gasdermin D fragments rapidly target the cell membrane of macrophages and permeabilize it by forming a pore. The porous membrane leads to cell swelling and bursting.”
Gasdermins cooperate in cell suicide
With gasdermin D, the researchers have not only identified the protein that deals a deathblow to immune cells, but they could also visualize pore formation using high-resolution microscopy techniques. As it turns out, following the cleavage of gasdermin D only one of the two fragments is required for the seamless integration into the cell membrane.
So far, only little is known about the gasdermin family of proteins, which along with gasdermin D includes five other members. In the future, Hiller’s team aims to investigate the structure and function of several gasdermins to determine whether and how they cooperate in pore formation and to identify the physiological context in which these proteins induce pyroptotic cell death.
Original source
Lorenzo Sborgi, Sebastian Rühl, Estefania Mulvihill, Joka Pipercevic, Rosalie Heilig, Henning Stahlberg, Christopher J. Farady, Daniel J. Müller, Petr Broz and Sebastian Hiller
GSDMD membrane pore formation constitutes the mechanism of pyroptotic cell death
EMBO Journal; published online 14 July 2016, doi: 10.15252/embj.201694696
Further information
Prof. Sebastian Hiller, University of Basel, Biozentrum, tel. +41 61 267 20 82, email: sebastian.hiller@unibas.ch
Dr. Katrin Bühler, University of Basel, Communications Biozentrum, Tel. +41 61 267 09 74, email: katrin.buehler@unibas.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



