Cellular 'backpacks' could treat disease while minimizing side effects
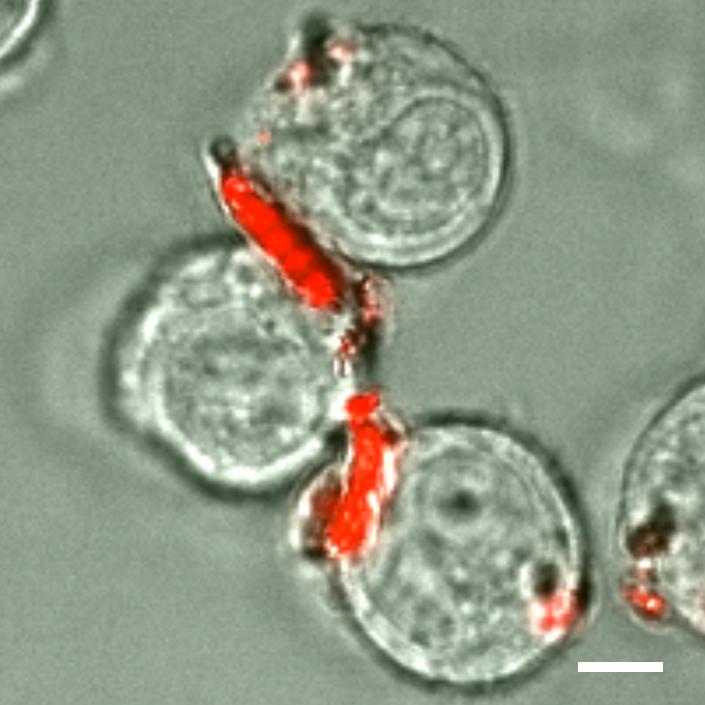
Monocytes -- a kind of white blood cell -- carry drug-loaded backpacks (red). (The scale bar is 5 micrometers.) Credit: Roberta Polak & Rosanna Lim
The researchers present their work today at the 251st National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS, the world's largest scientific society, is holding the meeting here through Thursday. It features more than 12,500 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“What we want to do is take advantage of immune cells whose job it is to seek out disease in the body, and use them to deliver cargo for us,” says Roberta Polak, a postdoctoral research associate. “How do we do that? Our lab developed cellular backpacks that can be loaded with therapeutic compounds and unloaded.”
Polak and fellow researchers in the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) labs of Michael Rubner, Ph.D., and Robert Cohen, Ph.D., make the backpacks by stacking ultra-thin layers of polymer materials on top of each other. According to Rubner, they could be used to treat a wide range of diseases from cancer to Parkinson's.
The resulting pack has different functional regions. One is Velcro-like, attaching via antibody-antigen binding to immune cells, such as monocytes and macrophages. These are the body's defense cells that travel to sites of inflammation — a natural reaction to infection and disease — and gobble up foreign invaders or attack cancer cells.
In vitro testing has shown that the backpacks can stick to the surfaces of the immune cells without getting engulfed. In collaboration with the group of Samir Mitragotri at the University of California at Santa Barbara, the MIT team has also demonstrated in mice that these backpack-functionalized immune cells accumulate in locations where inflammation — a sign of disease — occurs.
But there was a problem. The medicine they were using to test the backpacks, a cancer drug called doxorubicin, was leaking out — even during the initial fabrication process. So Polak worked on this part of the backpack, its payload region. To stop the premature release of the drug, she trapped it in liposomes, tiny bubbles that have already been used to carry therapeutic compounds for other delivery systems, and then incorporated them into the backpacks. She found that she could fit nine times the amount of doxorubicin in the liposomes than in the backpacks alone, potentially transforming them into an even more potent weapon.
To control the release of the drug payload, Polak used liposomes that are echogenic, or sensitive to ultrasound. So in principle, when backpacks infused with these bubbles reach their destination, they can be burst open with ultrasound waves.
Now, to see how well they work to treat a specific disease, Polak is collaborating with Elena Batrakova, Ph.D., at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Batrakova has been working with mice to develop new treatments for brain inflammation, a characteristic of diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. They want to see if they can use the backpacks to carry an inflammation-fighting enzyme across the blood-brain barrier.
###
A press conference on this topic will be held Wednesday, March 16, at 10 a.m. Pacific time in the San Diego Convention Center. Reporters may check-in at Room 16B (Mezzanine) in person, or watch live on YouTube http://bit.
Polak acknowledges funding from MIT's National Science Foundation Materials Research Science & Engineering Center.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 158,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research is being presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Title
Design and Production of Functional Thin-Film Backpacks for Cell-Based Therapies
Abstract
Cellular backpacks are 7-10 μm diameter polymer patches of a few hundred nanometers thickness that can be fabricated by using layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly onto a photopatterned substrate. Since backpacks can be attached to the surface of living cells without being phagocytized, our goal is to explore the use of backpacks for cell mediated and targeted drug-delivery. Cellular backpacks can be engineered to carry many different types of biologic and small molecule drugs. Additionally, by attaching the desired antibodies on the backpacks' surfaces, it is possible to adhere them to a wide variety of cells. Recent developments by our group have demonstrated the ability of backpack-monocyte conjugates to migrate and accumulate in inflamed tissue sites (e.g. lungs and skin). In this work, we show that the small molecule drug, doxorubicin, encapsulated into liposomes can be effectively embedded inside cellular backpacks. Drug release profiles from the backpacks show that using liposomes to encapsulate doxorubicin in the backpack leads to a 4-fold increase in drug loading compared to the drug loading without liposomes. The drug-loaded backpacks are then attached to mouse monocytes for studies with cells. Cytotoxicity assays shows that cell backpacks attached to monocytes do not significantly affect their viability. Because liposomes can carry a wide variety of drugs, this work demonstrates that liposomes can be used as drug depots as a versatile alternative for broadening the range of applications for cellular backpacks.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



