Chemists of TU Dresden develop highly porous material, more precious than diamonds
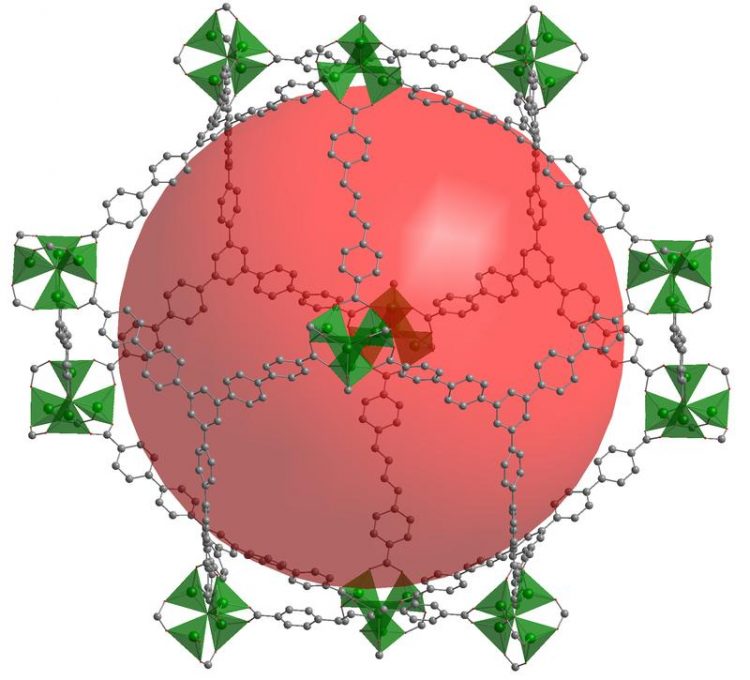
The framework of DUT-60 holds a pore volume of 5.02 cm3g-1 – the highest specific pore volume one has ever measured among all crystalline framework materials so far. Dr. I. Senkovska, TU Dresden
Porosity is the key to high-performance materials for energy storage systems, environmental technologies or catalysts: The more porous a solid state material is, the more liquids and gases it is able to store. However, a multitude of pores destabilizes the material.
In search of the stability limits of such frameworks, researchers of the TU Dresden’s Faculty of Chemistry broke a world record: DUT-60 is a new crystalline framework with the world’s highest specific surface and the highest specific pore volume (5.02 cm3g-1) measured so far among all known crystalline framework materials.
The specific surface area describes the sum of all surface boundaries a material has: the outer visible ones as well as the inner pores. 90.3% of DUT-60 is free volume. The metal-organic framework (MOF) can adsorb huge amounts of gas – and in that way it is able to store colossal quantities of gases or filter toxic gases from the air.
“Materials with specific surfaces as high as these could show new and unexpected phenomena,” explains Stefan Kaskel, Professor of Inorganic Chemistry at TU Dresden, the new material’s importance for science.
“If you imagine the inner surface of one gram of zeolite as an even, plane area, it would cover about 800 square metres, graphene would make it up to almost 3000 square metres. One gram of DUT-60 would attain an area of 7800 square metres.”
The material was developed by computational methods and synthesized subsequently. There are only few compounds of low density that are mechanically stable enough to be accessible for gases without their surfaces being destroyed.
“It took us five years from the computational development to the pure product DUT-60,” resumes Prof. Kaskel. “Due to its very complicated production, the material is more expensive than gold and diamonds and so far can be only synthesized in small quantities of maximum 50 milligram per batch.”
The former world record was held by the material NU-110 published by Omar Farha, Northwestern University, in 2012: Its pore volume of 4.40 cm3g-1 is significantly lower than the new record holder. DUT-60 marks an important step in the investigation of the upper limits of porosity in crystalline porous materials, and stimulates the development of new methods to determine inner surfaces.
Within the DFG Research Unit FOR2433, Prof. Kaskel and partners are working intensively on the production of new porous materials that can change their structures dynamically and adaptively adjust their pore sizes.
“Moreover, we are working on applications of porous materials within the fields of gas storage, environmental research, catalysis, batteries and air filtration. Here in Dresden, we are also producing metal organic frameworks on a scale of several kilograms. They can be ordered at the ‘Materials Center Dresden’.”
Prof. Dr. Stefan Kaskel
Chair of Inorganic Chemistry I
Tel: 0351/46334885
Mail: stefan.kaskel@tu-dresden.de
Angewandte Chemie: “Balancing Mechanical Stability and Ultrahigh Porosity in Crystalline Framework Materials”
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201808240 (International Edition)
https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201808240 (German Edition)
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.tu-dresden.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



