Chimpanzees help researchers improve machine learning of animal simulations
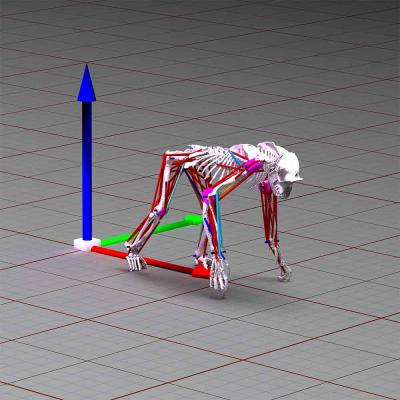
This is a cmputer simulation image of Chimpanzee walking used in research Credit: Bill Sellers
The research, being published by the Royal Society Open Science Journal, shows how simple changes to 'machine learning' algorithms can produce better looking, more accurate computer-generated animal simulations.
It will also help researchers investigate the 'curious way' that all primates walk and how this might be linked to stability whilst moving through the trees.
Professor Bill Sellers, from the School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, says: 'Starting from an animal's skeleton, computers using machine learning can now reconstruct how the animal could have moved. However, they don't always do a good job.
'But with some simple changes to the machine learning goals we can now create much more accurate simulations. We've now used this process to generate chimpanzee locomotion to explore why they walk the way they do.
'The idea was to look at how much energy it costs to walk in a stable fashion compared to other movement patterns.'
The chimpanzee model was created from a full body CT scan of an adult male common chimpanzee. Using the scan the team generated a skeletal model and a skin outline. The skeletal model was then used to define joint positions, muscle paths and limb contact points for the simulation.
This was then used to analyse the chimpanzee's gait, the pattern of movement animals (including humans) make whilst walking.
In evolutionary biomechanics – the study of evolution through movement processes – it is often thought that gaits of all animals evolved to use the least amount energy whilst travelling.
However, using the chimpanzee model, the research team are proving that this is no longer the case.
Prof Sellers explains: 'As technology has advanced and with musculoskeletal models becoming increasingly sophisticated, previous simulation models are becoming extremely unrealistic in relation to gait patterns so we have to adapt the way we think and research.'
The researchers found that by increasing lateral stability in the simulation it increases the energetic cost, but also the realism of the generated walking gait in a chimpanzee musculoskeletal model.
Prof Sellers added: 'The realism of the gait produced by the chimpanzee model is considerably enhanced by including a lateral stability and it is highly likely that this is an important evolutionary development.
'This enhanced lateral stability comes at a moderate energetic cost however, and this cost would need to be outweighed by other adaptive advantages.'
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



