Clues to ageing come to light in vivid snapshots of brain cell links
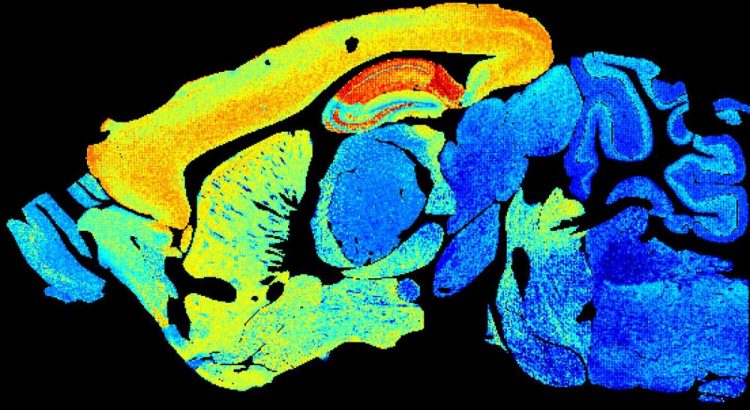
Adult mouse brain section showing increased synapse diversity. Credit Zhen Qui and Seth Grant University of Edinburgh. Credit: Zhen Qui and Seth Grant University of Edinburgh
Findings – published in the journal Science – could shed light on learning disability and dementia and help to reveal how memories are affected by age.
The images are of synapses – vital connections that carry electrical and chemical messages between brain cells. Synapses store memories and synapse damage is linked to more than 130 brain diseases.
Researchers based at the University of Edinburgh colour-coded the different types of molecules to highlight the range of synapses in mouse brains from birth to old age.
They discovered that the number and molecular makeup of synapses shifts with age in different parts of the brain. This happens at three main phases – childhood, middle and elderly age.
Synapse type shifts with age in patterns unique to areas of the brain, blossoming into a diverse array in midlife.
Images from middle-aged brains burst with colour, illustrating a wide variety of synapses. Both very young and very old brain show less synapses and less complexity.
Researchers say these changes give insights into why genes cause synapse damage at set ages and in set brain areas.
The findings could shed light on why we are more likely to develop brain conditions at certain ages, helping to explain why schizophrenia often starts in adolescence, or why dementia affects older adults.
The study was funded by Wellcome and the European Research Council.
Lead researcher, Professor Seth Grant of the Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences at the University of Edinburgh, said: “The brain is the most complex thing we know of and understanding it at this level of detail is a momentous step forward.
“We believe that these findings will be instrumental to helping understand why the brain is susceptible to disease at different times of life and how the brain changes as we age.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aba3163All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



