Computer simulations reveal roots of drug resistance
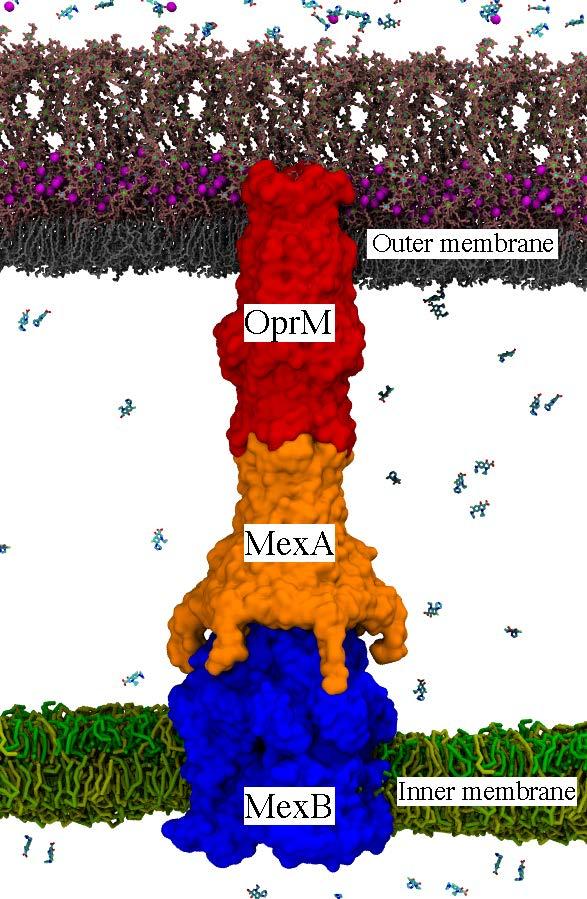
Bacterial efflux pumps, such as the P. aeruginosa MexAB-OprM pump shown here, are one of the dominant molecular mechanisms available to Gram-negative pathogens for removing toxins, including antibiotics. Inactivation of the pump assembly and function would be a major step for reducing bacterial multidrug resistance. Credit: LANL
New supercomputer simulations have revealed the role of transport proteins called efflux pumps in creating drug-resistance in bacteria, research that could lead to improving the drugs' effectiveness against life-threatening diseases and restoring the efficacy of defunct antibiotics.
“By understanding how the pump moves and dynamically behaves, we can potentially find a way to deactivate the pump–and antibiotics that haven't worked in a long time may be useful again,” said Los Alamos biophysicist Gnana Gnanakaran, who collaborated with colleagues at the Laboratory and with bacterial efflux pump experts Helen Zgurskaya at the University of Oklahoma and Klaas Pos at Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany.
Some life-threatening infections do not respond to antibiotics because efflux pumps inside a particular type of infectious microbe called Gram-negative bacteria flush out antibiotics before the drugs can work. One type of efflux pump, which until recently had only been studied in parts, was recently modeled in its entirety and simulated using supercomputers at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
The findings, published November 28 in Scientific Reports, offer a better understanding of the motions and functions of efflux pumps. The work exploits the Laboratory's extensive modeling and supercomputing simulation capabilities developed in support of its national security mission.
For this study, the researchers focused on efflux pumps inside the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which can cause serious illnesses such as pneumonia and sepsis. In P. aeruginosa, the major pump type is called MexAB-OprM and composed of three proteins: MexA, MexB and OprM.
“This is a really, really large system–approximately a million and a half atoms,” said Laboratory theoretical biologist Cesar A. López. The MexAB-OprM pump encompasses both inner and outer membranes found in Gram-negative bacteria and connects the cell's interior and periplasm (the compartment between both membranes) to the cell's exterior. That connection creates a path for drug molecules to exit the cell.
The Laboratory's supercomputers were able to perform the first atomistic simulations of the entire MexAB-OprM pump embedded within a double membrane system on a microsecond time scale.
The researchers then used the simulations to investigate the dynamics of the assembled pump and to understand how pump functionality arises from these dynamics. The amino acid interactions that stabilize the complex between MexA and OprM were also independently cross-validated using a computational technique called sequence covariation analysis by Laboratory theoretical biologist Timothy Travers. According to Travers, “This is the first time such a sequence-based technique has been applied for cross-validating the interface of a protein complex built using simulations and cryo-electron microscopy.”
Application of these computational techniques to the multitude of efflux pumps found in different Gram-negative pathogens should allow scientists to elucidate if general mechanisms are shared among different pumps or are pump-specific. For example, perhaps the amino acid interactions that stabilize the pump structure could be targeted by drug development efforts to block pump assembly or function, thereby rendering currently defunct antibiotics effective once more.
###
The paper: “Dynamics of Intact MexAB-OprM Efflux Pump: Focusing on the MexA-OprM Interface,” Scientific Reports, https:/
The funding: LDRD-DR
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, BWX Technologies, Inc. and URS Corporation for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration. Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health and global security concerns.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



