Computing with molecules: a big step in molecular spintronics
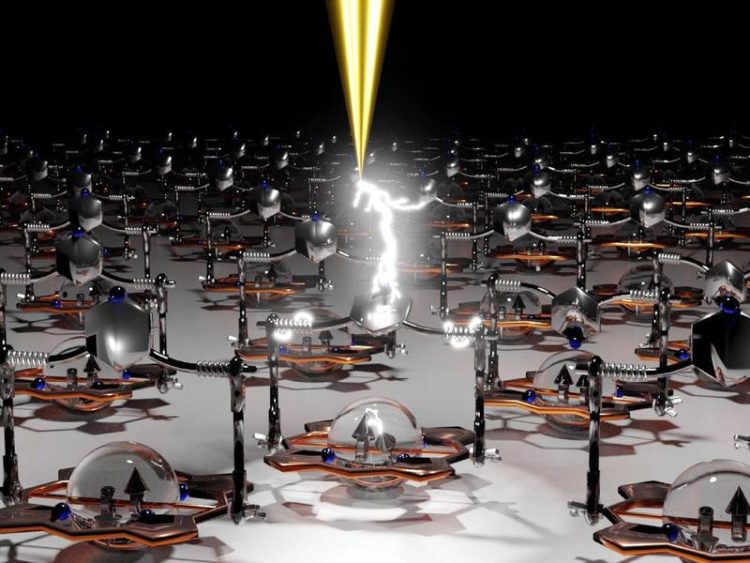
Each molecule can be separately addressed with a scanning tunneling microscope and switched between the states by applying a positive or negative voltage. © Jan-Simon von Glasenapp and Rainer Herges
Spintronics or spin electronics in contrast to conventional electronics uses the spin of electrons for sensing, information storage, transport, and processing. Potential advantages are nonvolatility, increased data processing speed, decreased electric power consumption, and higher integration densities compared to conventional semiconductor devices.
Molecular spintronics aims for the ultimate step towards miniaturization of spintronics by striving to actively control the spin states of individual molecules. Chemists and physicists at Kiel University joined forces with colleagues from France, and Switzerland to design, deposit and operate single molecular spin switches on surfaces.
The newly developed molecules feature stable spin states and do not lose their functionality upon adsorption on surfaces. They present their results in the current issue of the renowned journal Nature Nanotechnology.
The spin states of the new compounds are stable for at least several days. “This is achieved by a design trick that resembles the fundamental electronic circuits in computers, the so-called flip-flops. Bistability or switching between 0 and 1 is realized by looping the output signal back to the input”, says experimental physicist Dr. Manuel Gruber from Kiel University.
The new molecules have three properties that are coupled with each other in such a feedback loop: their shape (planar or flat), the proximity of two subunits, called coordination (yes or no), and the spin state (high-spin or low-spin). Thus, the molecules are locked either in one or the other state. Upon sublimation and deposition on a silver surface, the switches self-assemble into highly ordered arrays. Each molecule in such an array can be separately addressed with a scanning tunneling microscope and switched between the states by applying a positive or negative voltage.
„Our new spin switch realizes in just one molecule what takes several components like transistors and resistors in conventional electronics. That’s a big step towards further miniaturisation”, Dr. Manuel Gruber und organic chemist Prof. Dr. Rainer Herges explain. The next step will be to increase the complexity of the compounds to implement more sophisticated operations.
Molecules are the smallest constructions that can be designed and built with atomic precision and predictable properties. Their response to electrical or optical stimuli and their custom-designed chemical and physical functionality make them unique candidates to develop new classes of devices such as controllable surface catalysts or optical devices.
Original publication:
Alexander Köbke, Florian Gutzeit, Fynn Röhricht, Alexander Schlimm, Jan Grunwald, Felix Tuczek, Michal Studniarek, Danilo Longo, Fadi Choueikani, Edwige Otero, Philippe Ohresser, Sebastian Rohlf, Sven Johannsen, Florian Diekmann, Kai Rossnagel, Alexander Weismann, Torben Jasper-Toennies, Christian Näther, Rainer Herges, Richard Berndt, Manuel Gruber, Reversible coordination-induced spin-state switching in complexes on metal surfaces, Nature Nanotechnology (2019), DOI: 10.1038/s41565-019-0594-8
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-019-0594-8
Pictures for Download:
https://www.uni-kiel.de/de/pressemitteilungen/2019/414-spintronik-1.jpg
Caption: Each molecule can be separately addressed with a scanning tunneling microscope and switched between the states by applying a positive or negative voltage.
© Jan-Simon von Glasenapp and Rainer Herges
https://www.uni-kiel.de/de/pressemitteilungen/2019/414-spintronik-2.jpg
Caption: The new molecule has three properties. Only two combinations of these properties are stable. Switched between the different states is achieved by applying tiny tunneling currents.
© Rainer Herges
Kontakt:
Prof. Dr. Rainer Herges
Otto Diels Institute of Organic Chemistry
Tel. +49 (0)431 880 2440
Mail: rherges@oc.uni-kiel.de
Web: https://www.otto-diels-institut.de/en/otto-diels-institute-of-organic-chemistry
Dr. rer. nat. Manuel Gruber
Oberflächenphysik
Tel. +49 (0)431 880 5091
Mail: gruber@physik.uni-kiel.de
Web: http://www.ieap.uni-kiel.de/surface
The project was supported by CRC 677 „Function by Switching“, which was funded in the period 2007-2019 by the German Research Foundation at CAU in Kiel.
More information about research area KiNSIS
Details, which are only a millionth of a millimetre in size: this is what the priority research area “Kiel Nano, Surface and Interface Science – KiNSIS” at Kiel University has been working on. In the nano-cosmos, different laws prevail than in the macroscopic world – those of quantum physics. Through intensive, interdisciplinary cooperation between physics, chemistry, engineering and life sciences, the priority research area aims to understand the systems in this dimension and to implement the findings in an application-oriented manner. Molecular machines, innovative sensors, bionic materials, quantum computers, advanced therapies and much more could be the result. More information at www.kinsis.uni-kiel.de
Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel
Presse, Kommunikation und Marketing, Dr. Boris Pawlowski
Postanschrift: D-24098 Kiel, Telefon: (0431) 880-2104, Telefax: (0431) 880-1355
E-Mail: presse@uv.uni-kiel.de Internet: www.uni-kiel.de Twitter: www.twitter.com/kieluni
Facebook: www.facebook.com/kieluni Instagram: www.instagram.com/kieluni
Prof. Dr. Rainer Herges
Otto Diels Institute of Organic Chemistry
Tel. +49 (0)431 880 2440
Mail: rherges@oc.uni-kiel.de
Web: https://www.otto-diels-institut.de/en/otto-diels-institute-of-organic-chemistry
Dr. rer. nat. Manuel Gruber
Surface Physics
Tel. +49 (0)431 880 5091
Mail: gruber@physik.uni-kiel.de
Web: http://www.ieap.uni-kiel.de/surface
Alexander Köbke, Florian Gutzeit, Fynn Röhricht, Alexander Schlimm, Jan Grunwald, Felix Tuczek, Michal Studniarek, Danilo Longo, Fadi Choueikani, Edwige Otero, Philippe Ohresser, Sebastian Rohlf, Sven Johannsen, Florian Diekmann, Kai Rossnagel, Alexander Weismann, Torben Jasper-Toennies, Christian Näther, Rainer Herges, Richard Berndt, Manuel Gruber, Reversible coordination-induced spin-state switching in complexes on metal surfaces, Nature Nanotechnology (2019), DOI: 10.1038/s41565-019-0594-8
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-019-0594-8
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



