CSD-Materials suite provides a cohesive analysis of solid form properties
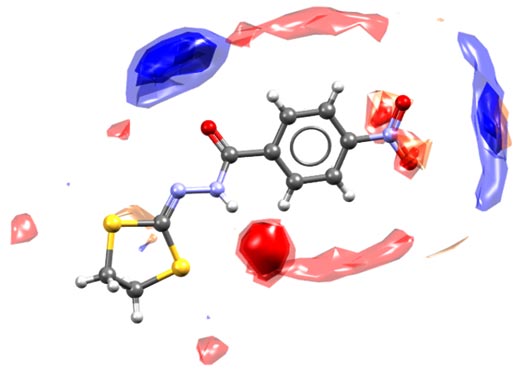
A full interaction map (FIM) for the Cambridge Structural Database entry DEDMUX, a potential tuberculostatic agent. This FIM compares the observed intermolecular interactions with preferred geometries for that type of interaction. The red regions of the map denote areas where there is a high probability of a hydrogen bond acceptor, the blue regions denote hydrogen bond donors, and the brown regions indicate hydrophobic preferences. DOI: 10.5517/ccdc.csd.cc1prpw0.
Credit: Ghazala Sadiq, CCDC Scientific Liaison and Senior Scientist
… for early-phase drug discovery.
The existence of various molecular arrangements that occur in the solid-state is called polymorphism. During early-phase drug discovery, researchers commonly look at hydrogen-bonding networks to identify potential metastable polymorphs. But what if a system doesn’t have hydrogen bonding? Or what if the hydrogen-bonding networks are the same in two different solid forms?
Going beyond hydrogen-bonding networks with CSD-Materials
CCDC’s CSD-Materials suite provides a comprehensive analysis of a potential active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) that helps researchers explore and analyse intra- and intermolecular interactions within the lattice. Along with Hydrogen Bond Propensity, the suite features components with applications in early-phase drug discovery, including Full Interaction Maps (FIMs) and an Aromatics Analyser. These can prove especially helpful when hydrogen-bonding networks cannot fully distinguish polymorph stability.
Full Interaction Maps (FIMs) highlight interaction preferences
FIMs provide a molecule’s interaction preferences in the context of the observed crystal structure—generating an intuitive, 3D visualization of the molecule’s preferred interactions and the intermolecular packing of the crystal structure. This can help identify potential co-former or solvent interactions for a new API. The component calculates regions around the molecule where chemical probe groups are likely to be found using the empirically derived, expert-curated data in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD). The CSD is the world’s repository for small-molecule organic and metal-organic crystal structures—containing over 1.1 million structures from X-ray and neutron diffraction analyses.
Aromatics Analyser identifies stabilizing interactions
The Aromatics Analyser enables the quantitative assessment of aromatic ring interactions and is CCDC’s first component based on a neural network. The model scores the strength of an aromatic interaction between two phenyl rings using quantum mechanics and the rings’ relative positions, highlighting any likely contribution to the stability of a crystal structure. Sometimes the dominant interactions stabilizing a system are solvent dependent. The Aromatics Analyser can specifically help in these cases, as well as when hydrogen-bonding networks alone cannot distinguish between solid forms.
Case Study: AstraZeneca leverages CSD-Materials to de-risk solid form selection in early-phase drug development
In a recent paper published in Crystal Growth & Design, researchers at AstraZeneca applied the CSD-Materials suite—specifically the Hydrogen Bond Propensity, FIMs, and Aromatics Analyser components—to de-risk the solid-state forms of a potential asset for immune-mediated diseases.
In this work, the authors first analysed the hydrogen-bonding networks of two solid forms with the Hydrogen Bond Propensity tool. Dr Okky Dwichandra Putra is a co-author on the paper and Associate Principal Scientist in Early Product Development and Manufacturing at AstraZeneca.
“Typically, we observe that the propensity tool can discriminate among hydrogen bond propensities to indicate possible risks,” Putra says. “However, it is not uncommon to see that hydrogen bond propensities overlap. This is also dependent on the propensity ranges and how much they overlap with each other. And as molecules become more complex there will be more competitive sites for hydrogen bonding.”
As a result, he says it’s standard for the team to also run a dispersion-corrected, density-functional theory (DFT) calculation, and for the team to use the Aromatics Analyser and FIMs components of CSD-Materials. These methods were all used to analyse two key forms in the paper. Both the Aromatics Analyser tool and the DFT calculations showed the importance of considering aromatic interactions, especially in what was deemed the most pharmaceutically viable solid form.
“We have found that stacking and other dispersion interactions play important roles in stabilizing crystal structures and for crystal growth,” Putra says. “So, it is critical to get the overall interactions described and not only hydrogen bonding.”
Read the paper: Putra, O.D. et al. Crys. Growth Des. 2022 22 (1), 535-546. DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.1c01124
Journal: Crystal Growth & Design
DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.1c01124
Article Title: Understanding crystal structures to guide form selection of active pharmaceutical ingredients: A case study of AZD9567
Article Publication Date: 21-Dec-2021
Media Contact
Ashley Moreno
CCDC – Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre
amoreno@ccdc.cam.ac.uk
Office: 512-375-0082
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



