Double trouble: A drug for alcoholism can also treat cancer by targeting macrophages
An anti-alcoholism drug--disulfiram, it may be possible to disrupt tumor progression. Credit: Tokyo University of Science
Developing a therapy to combat cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in medical research. Cancer owes its notorious identity to the fact that the cancer cells use the host's own immune system to grow and spread, ultimately becoming deadly.
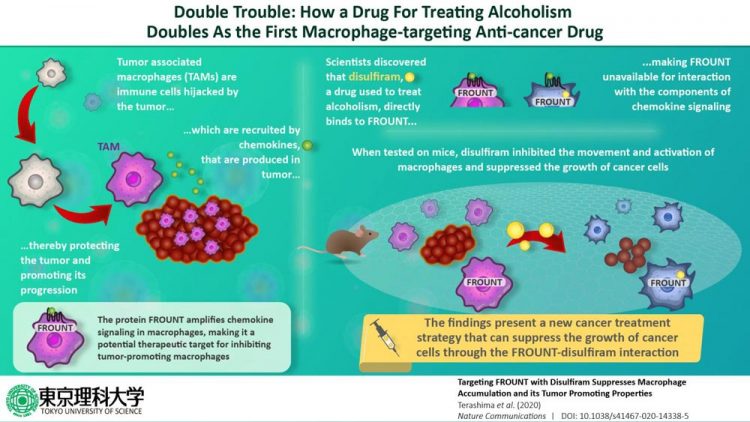
Immune cells like macrophages, which ordinarily fight to protect normal cells, are hijacked by malignant cancer cells, and populate the environment around the tumors, becoming tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs).
In fact, it was found that the cancerous tissue of patients for whom immunotherapy was not successful was indeed rich in macrophages, confirming the link between the cancer and the TAMs.
It is these TAMs that produce signaling proteins like chemokines and trigger the inhibitory immune checkpoint releases that create an immunosuppressive tumor environment, which protects the cancer cells and allows their accelerated growth. Since it is the TAMs that facilitate the spreading of cancer cells, regulating them as a therapeutic strategy for combating cancer has gained attention in recent years.
A research group led by Yuya Terashima from the Tokyo University of Science saw this as an opportunity to explore the realm of developing novel anti-cancer drugs. Their seminal work in Nature Immunology 2005 reported the discovery of a new target protein called FROUNT, which is linked to regulation and movement of the TAMs.
Since FROUNT amplified “chemokine signaling,” a type of cellular communication, an integral process for TAM accumulation and activity, it was therefore linked directly to TAM regulation.
The team decided to expand on these findings, in order to investigate whether a therapeutic strategy can be formulated and have published their findings in Nature Communications. Through animal experiments, the researchers found that by regulating FROUNT expression in TAMs, cancer growth could be suppressed.
Then, in order to reduce any side effects, the team also developed an independent strategy of limiting the effect of FROUNT on chemokine signaling by inhibiting the interaction between the two. The team screened 131,200 compounds and zeroed in on disulfiram, a drug used to treat alcoholism, and known for its potential as an anti-cancer drug. This drug was found to directly bind to the FROUNT site, making FROUNT unavailable for interaction with the components of chemokine signaling.
Reflecting on the results, Terashima explains, “When tested on mice, disulfiram inhibited the movement of macrophages and suppressed the growth of cancer cells. Therefore, our findings present a new cancer treatment strategy that can suppress the growth of cancer cells that are difficult to respond to by immune checkpoints when used in combination with disulfiram.”
The team is now further pushing the boundary of the finding and has started clinical research at the National Cancer Center Hospital East. Illustrating the outline for further research, Terashima comments, “since macrophages pose as a problem in various types of diseases, the indications for FROUNT inhibitors for a wide range of diseases may be considered.”
Indeed, the team expects this this to be the first therapeutic strategy to regulate TAMS, and are hopeful that a better understanding of the correlation between the inhibition of the target protein FROUNT and TAMs paint a promising picture for the future of novel therapeutic strategies.
###
About The Tokyo University of Science
Tokyo University of Science (TUS) is a well-known and respected university, and the largest science-specialized private research university in Japan, with four campuses in central Tokyo and its suburbs and in Hokkaido. Established in 1881, the university has continually contributed to Japan's development in science through inculcating the love for science in researchers, technicians, and educators.
With a mission of “Creating science and technology for the harmonious development of nature, human beings, and society”, TUS has undertaken a wide range of research from basic to applied science. TUS has embraced a multidisciplinary approach to research and undertaken intensive study in some of today's most vital fields. TUS is a meritocracy where the best in science is recognized and nurtured. It is the only private university in Japan that has produced a Nobel Prize winner and the only private university in Asia to produce Nobel Prize winners within the natural sciences field.
Website: https:/
About Dr. Terashima from Tokyo University of Science
Dr. Yuya Terashima is a junior associate professor at the Department of Biological Sciences, Tokyo University of Science. He discovered a chemokine signal regulator FROUNT which directly binds to the receptor, and has been studying for the family of the chemokine-receptor associating molecule, aiming for therapeutic applications of their functional inhibitors. He works with his team to understand the molecular mechanisms of living organisms with a specific perspective on inflammation and immunology, and drug discovery.
Funding information
This study was supported in part by Practical Research for Innovative Center Control (JP19ck0106422) and Project for Cancer Research and Therapeutic Evolution (P-CREATE, JP19cm0106204) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) and JSPS KEKENHI.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14338-5All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



