Dramatic transition in Streptomyces life cycle explained in new discovery
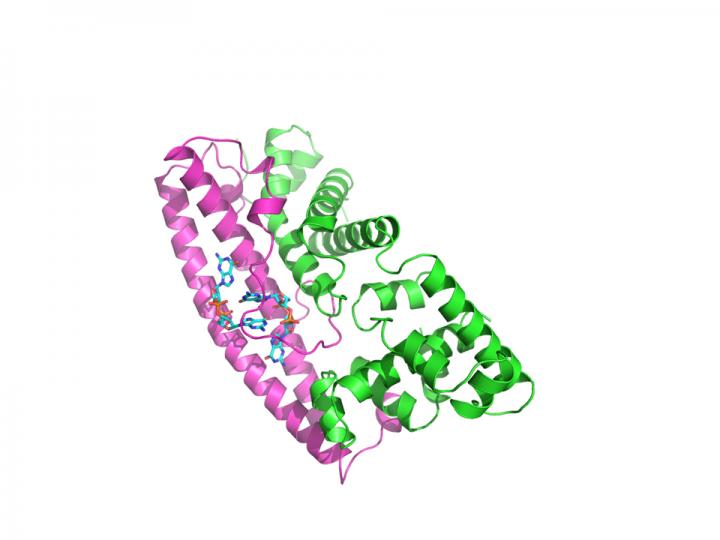
Protein interaction structures - Streptomyces Credit: John Innes Centre
Previous research by Professor Mark Buttner's lab at the John Innes Centre has shown that the signalling molecule c-di-GMP binds BldD, a master repressor of gene activity, to control the initiation of development in these soil-dwelling bacteria.
c-di-GMP is an example of a nucleotide second messenger, an intracellular signal widespread in bacteria responsible for regulating crucial processes, including mobility, virulence and biofilm formation.
In a new study, experiments using the model species Streptomyces venezuelae show that c-di-GMP also intervenes later in development to control the differentiation of the reproductive hyphae into spores.
It does this by mediating an interaction between the major sporulation sigma factor in Streptomyces, WhiG, and the anti-sigma factor RsiG.
A sigma factor is a protein needed for the initiation of transcription, the process of turning DNA into RNA. Anti-sigma factors bind to the sigma and inhibit activity until the time is appropriate.
The study shows that RsiG and c-di-GMP bind and hide sigma WhiG, preventing its target genes being expressed and therefore stopping the reproductive hyphae turning into spores.
It is the first instance of c-di-GMP binding to a sigma factor and affecting its functionality.
First author of the study Dr Kelley Gallagher says: “As a result of this discovery, it is now clear that c-di-GMP signals through BldD and sigma WhiG respectively to control the two most dramatic transitions of the Streptomyces life cycle, the formation of the reproductive aerial hyphae and their differentiation into spore chains. In both cases, c-di-GMP functions as a brake.”
###
“c-di-GMP arms an anti-σ to control progression of multicellular differentiation in Streptomyces” appears in the journal Molecular Cell
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.11.006All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



