EU project for the development of Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever virus (CCHFV) vaccines starts
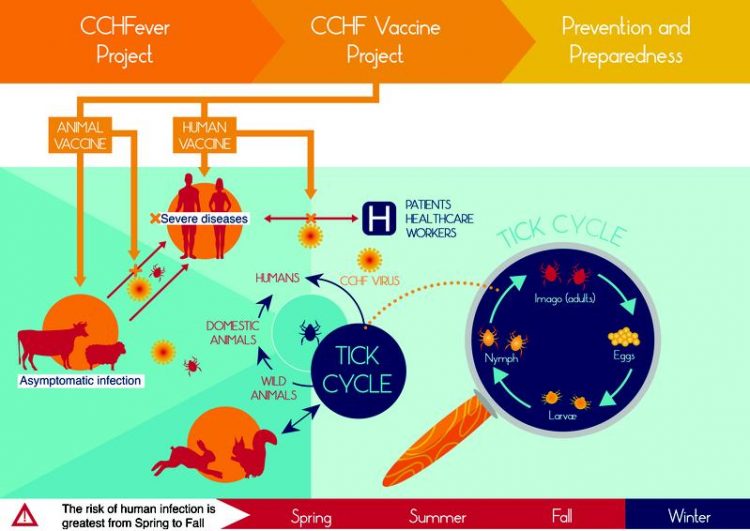
Transmission cycle of Crimean Congo Haemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) Source:CCHF Vaccine
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever is cause by the Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic virus (CCHFV). Ruminants constitute the primary viral reservoir. CCHFV is wide-spread and occurs in various countries in Europe, Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. The virus is transmitted by ticks and the close contact with infected blood or tissue.
Infected animals generally do not show any signs of disease, whereas patients develop flu-like symptoms with fever, muscle and limb ache, as well as neurological and gastrointestinal signs. A subset of those affected develop serious haemorrhagies, and the mortality rate lies around 30 percent. Up to now, neither effective antiviral treatments nor licensed vaccines are available.
The CCHFVaccine Project aims at stepping up efforts to develop and provide vaccines against CCHFV for humans and animals thereby using an One Health approach as already exemplified by the participation of both major German medical and veterinary infectious disease research institutes.
Vaccination of susceptible animals will be pursued to reduce the viral burden, whereas vaccine development for humans primarily aims at the protection of individuals at high risk for exposure. The project consortium is funded with six million € for a period of six years within the scope of the European research and innovation programme “Horizon 2020” (see below).
The CCHFVaccine Consortium is led by Professor Ali Mirazimi at the Swedish Health Agency, the Karolinska Institute, and the Swedish National Veterinary Institute. The Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, which is the competent authority for the authorisation of clinical trials, marketing authorisations, and official batch control in Germany, will provide expert advice in regulatory aspects.
The Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut, Federal Research Institute for Animal Health, Island of Riems will assess the efficacies of newly developed animal vaccines by challenging cattle in the unique newly commissioned BSL4 high containment laboratory and animal facility. The third German partner involved is the Justus-Liebig University, which is specialised in vaccine design.
Horizon 2020
Horizon 2020 is the framework programme of the European Union for research and innovation. It promotes research, and as such, aims at developing a knowledge- and innovation-driven society and a competitive economy. At the same time it has the purpose of contributing to sustained development. In addition to the member states of the European Union, various other countries can participate in the Horizon 2020 program.
The Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, the Federal Institute for Vaccines and Biomedicines, in Langen near Frankfurt/Main is a senior federal authority reporting to the Federal Ministry of Health (Bundesministerium für Gesundheit, BMG). It is responsible for the research, assessment, and marketing authorisation of biomedicines for human use and immunological veterinary medicinal products. Its remit also includes the authorisation of clinical trials and pharmacovigilance, i.e. recording and evaluation of potential adverse effects.
Other duties of the institute include official batch control, scientific advice and inspections. In-house experimental research in the field of biomedicines and life science form an indispensable basis for the manifold tasks performed at the institute.
The Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, with its roughly 800 members of staff, also has advisory functions nationally (federal government, federal states (Länder)), and internationally (World Health Organisation, European Medicines Agency, European Commission, Council of Europe etc.).
http://fli.bund.de – FLI Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut
http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/207211_en.html – CORDIS Project Information
https://www.uni-giessen.de/research/research-organizations/eu-projects/cooperati… – CCHFV-Projekt Info of Justus Liebig University Gießen
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



