Every grain of sand is a metropolis for bacteria
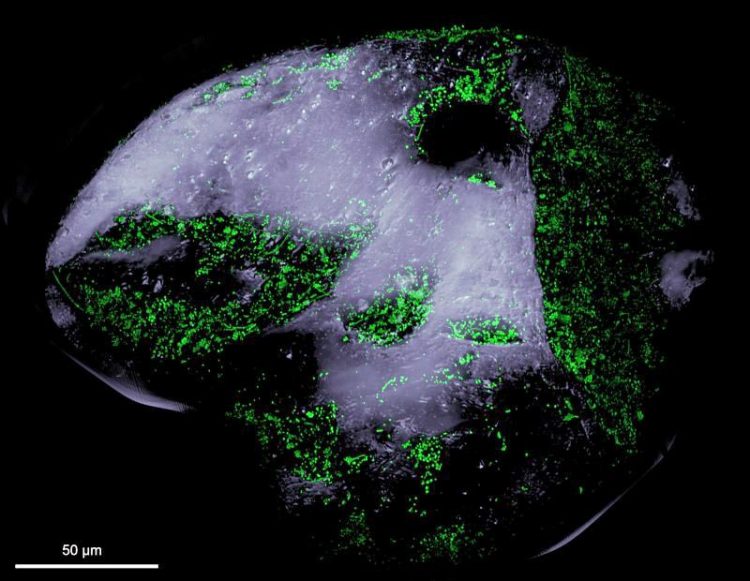
View of a sand grain under a fluorescence microscope: The green spots are stained bacteria, which have mainly colonized depressions on the grain. Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology/CC-SA BY 4.0
Just imagine, you are sitting on a sunny beach, contentedly letting the warm sand trickle through your fingers. Millions of sand grains. What you probably can't imagine: at the same time, billions upon billions of bacteria are also trickling through your fingers.
Between 10,000 and 100,000 microorganisms live on each single grain of sand, as revealed in a study by researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen. This means that an individual grain of sand can have twice as many residents as, say, the city of Fairbanks, Alaska!
Even bacteria hide
It has long been known that sand is a densely populated and active habitat. Now David Probandt and his colleagues have described the microbial community on a single grain of sand using modern molecular methods. To do this, they used samples taken from the southern North Sea, near the island of Heligoland, off the German coast.
The bacteria do not colonize the sand grains uniformly. While exposed areas are practically uncolonized, the bacteria bustle in cracks and depressions. “They are well protected there”, explains Probandt. “When water flows around the grains of sand and they are swirled around, rubbing against each other, the bacteria are safe within these depressions.” These sites may also act as hiding grounds from predators, who comb the surface of the sand grains in search of food.
Impressive diversity
However, the diversity of the bacteria, and not just their numbers, is impressive. “We found thousands of different species of bacteria on each individual grain of sand”, says Probandt.
Some bacteria species and groups can be found on all investigated sand grains, others only here and there. “More than half of the inhabitants on all grains are the same. We assume that this core community on all sand grains displays a similar function”, explains Probandt. “In principle, each grain has the same fundamental population and infrastructure.” We can therefore really discover a great deal about the bacterial diversity of sand in general from investigating a single grain of sand.
Sandy coasts are enormous filters
Sand-dwelling bacteria play an important role in the marine ecosystem and global material cycles. Because these bacteria process, for example, carbon and nitrogen compounds from seawater and fluvial inflows, the sand acts as an enormous purifying filter. Much of what is flushed into the seabed by seawater doesn't come back out.
“Every grain of sand functions like a small bacterial pantry”, explains Probandt. They deliver the necessary supplies to keep the carbon, nitrogen and sulphur cycles running. “Whatever the conditions may be that the bacterial community on a grain of sand is exposed to – thanks to the great diversity of the core community there is always someone to process the substances from the surrounding water.”
Original publication
Probandt, T. Eickhorst, A. Ellrott, R. Amann and Katrin Knittel (2017): Microbial life on a sand grain: from bulk sediment to single grains. The ISME Journal.
DOI:10.1038/ismej.2017.197
Published under CC-SA BY 4.0
Additional information
Probandt, D., Knittel, K., Tegetmeyer, H. E., Ahmerkamp, S., Holtappels, M. and Amann, R. (2017): Permeability shapes bacterial communities in sublittoral surface sediments. Environ Microbiol, 19: 1584–1599. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13676
Please direct your queries to
David Probandt
Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology
Phone: +49 421 2028 940
E-Mail: dprobandt@mpi-bremen.de
Dr. Katrin Knittel
Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology
Phone: +49 421 2028 935
E-Mail: kknitel@mpi-bremen.de
or the press office
E-Mail: presse(at)mpi-bremen.de
Dr. Fanni Aspetsberger
Telefon: +49 421 2028 947
Dr. Manfred Schlösser
Phone: +49 421 2028 734
http://www.mpi-bremen.de
https://www.nature.com/articles/ismej2017197
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



