Exeter biologists investigate smallest propeller on earth
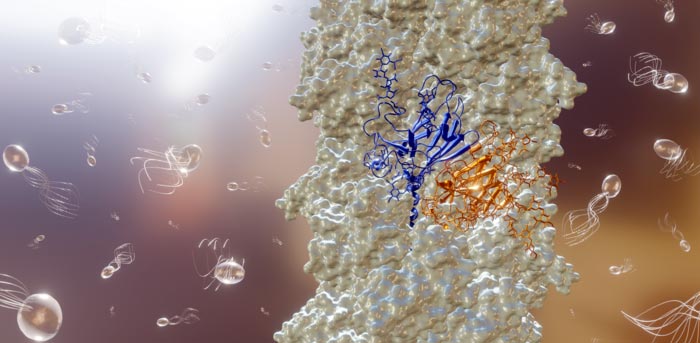
Representation of the M. villous archaellum highlighting the two alternating subunits in blue and orange (foreground) and swimming M. villosus cells (background)
Credit: University of Exeter
University of Exeter scientists have discovered new information about the tiny propellers used by single-cell organisms called archaea.
Like bacteria, archaea are found in a vast range of habitats – including inside human bodies – but unlike bacteria they are not known to cause disease.
Some archaea propel themselves to incredible speeds by rotating a spiral-shaped filament called an archaellum.
Using a powerful cryo-electron microscope, the new study examined this closer than ever before.
The research team – which included the University of Regensburg – focussed on Methanocaldococcus villosus, a species found near underwater volcanoes off Iceland, where water temperatures can reach about 80°C.
“M. villosus swims at a speed of about 500 body lengths per second,” said Dr Lavinia Gambelli, of Exeter’s Living Systems Institute (LSI).
“Considering that the tiny cell is only about one micrometre in size, this means half a millimetre in one second.
“At first glance, this does not seem much.
“But in comparison, a cheetah achieves only 20 body lengths per second – so if an M. villosus cell had the size of a cheetah, it would swim at approximately 3,000 kilometres per hour.
“The incredible speed that M. villosus can achieve makes it one of the fastest organisms on the planet.”
Using the cryo-electron microscope, researchers can see objects whose width is as small as only a few hydrogen atoms.
“At this resolution, we can see the very fabric of life and study fundamental biological processes at atomic detail,” said Dr Bertram Daum, also of the LSI.
“In this study, we were able to look closely at the smallest propeller in the world, to find out more about its shape and how it works.
“As well as teaching us more about these fascinating organisms, this could have implications for human health and technology.
“Archaea make up a considerable percentage of the microorganisms found in the human body. None has so far been found to cause disease, but it remains a possibility.
“In the future, it might even be possible to develop microscopic robotic devices for drug delivery based on the tiny propellers used by archaea.”
The study discovered that the filament used by M. villosus is made up of thousands of copies of two alternating proteins, whereas previously investigated filaments showed only one protein.
This suggests that the architecture and assembly of an archaellum is more complex than previously thought.
The researchers also identified two major structural elements that enable the archaellum filament to move, propelling the cell at high speed.
The study was funded by the European Research Council.
The paper, published in the journal Nature Communications, is entitled: “An archaellum filament composed of two alternating subunits.”
Journal: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28337-1
Method of Research: Observational study
Subject of Research: Cells
Article Title: An archaellum filament composed of two alternating subunits
Article Publication Date: 7-Feb-2022
Media Contact
Louise Vennells
University of Exeter
pressoffice@exeter.ac.uk
Office: 0044-139-272-2062
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



