Fast lab-on-chip detects effects of poison
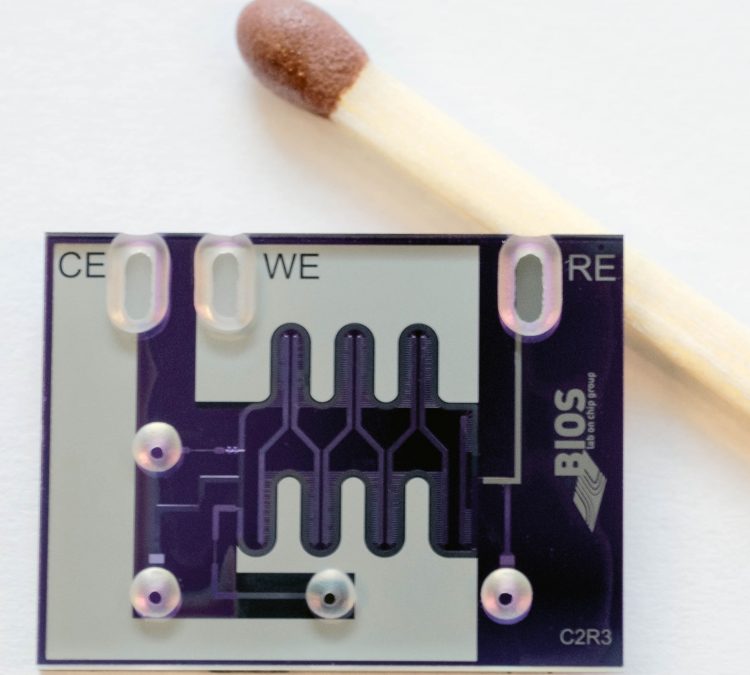
The full reactor and mixing unit on a chip
The effect that toxic substances have on, for example, hemoglobin in blood, can now be tested in a fast way using a new lab-on-a-chip. University of Twente scientist Floris van den Brink developed a fast and efficient mixer for this.
Substances foreign to the human body – toxic substances, or medication, for example – can have such a short lifetime that the effect is hard to examine. Sometimes the damage already has been done. For example: what happens if PAH’s, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons interact with hemoglobin in blood?
PAH’s are released at asphalt road works or coal power plants, for example. Using his new lab-on-a-chip system, Floris van den Brink is able to examine this fast interaction, just like in the human body.
Our body, especially the liver, converts these foreign substances into metabolites. The chip does this as well: a tiny electrochemical reactor produces PAH metabolites like hydroxypyrene. The next step is mixing these metabolites with hemoglobine, to see in what way the toxic and highly reactive metabolite binds to hemoglobin. Using a new mixing technique, this can be done very fast: well within a second.
Using the same micro laboratory, possible remedies can be examined as well, for detoxing the blood. In this way, the chip can also be used for measuring the effects of medication without the need of using laboratory animals.
Rapid mixing
Mixing of fluids on a micro or nano scale is not trivial: they behave differently in the tiny fluid channels, and mechanical stirring is not an option. Van den Brink therefore designed two circular mixing chambers, consisting of tiny channels that have a gradient. One substance enters above, the other below. Using the angle difference, mixing can be accelerated substantially. The entire mixer is no bigger than 0.1 square millimeter. Using mass spectrometry, the output is analysed. The reactor is also special: using diamond electrodes in stead of platinum ones, the yield is improved.
Proteomics
Measuring the effect of hydroxypyrene metabolites on hemoglobine is just one example of the possible applications of the new chip. The system is suitable for analysing numerous types of interactions with proteins, possibly DNA as well. As proteomics is gaining importance in the development of medicine, the chip is a fast and powerful tool.
Van den Brink did his research in the BIOS Lab-on-a-Chip group, part of University of Twente’s MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology and MIRA Institute for Biomedical Technology and Technical Medicine. He collaborated with colleagues of the University of Münster, Germany.
For further information, please contact:
Wiebe van der Veen
+31612185692
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Retinoblastoma: Eye-Catching Investigation into Retinal Tumor Cells
A research team from the Medical Faculty of the University of Duisburg-Essen and the University Hospital Essen has developed a new cell culture model that can be used to better…

A Job Well Done: How Hiroshima’s Groundwater Strategy Helped Manage Floods
Converting Disasters into Opportunities Society is often vulnerable to disasters, but how humans manage during and after can turn devastation into opportunities for improved resilience. An Alternative Water Source: Private…

Shaping the Future: DNA Nanorobots That Can Modify Synthetic Cells
Scientists at the University of Stuttgart have succeeded in controlling the structure and function of biological membranes with the help of “DNA origami”. The system they developed may facilitate the…



