First study on physical properties of giant cancer cells may inform new treatments
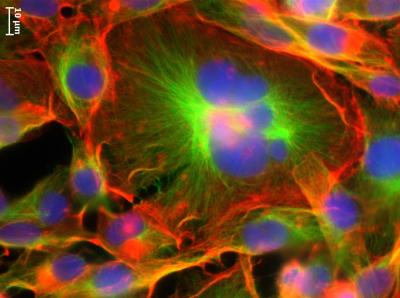
Polyploidal "giant" cancer cells are seen in the middle surrounded by other types of smaller cancer cells. The cells' nuclei are dyed blue. Actin, the cable-like structures that enable cells to move, is dyed red. Credit: Michelle Dawson / Brown University
The research, published Aug. 9 in Scientific Reports, shows that the giant cells are stiffer and have the ability to move further than other cancer cells, which could help explain why they're associated with more serious disease.
“I think these polyploidal giant cancer cells are the missing link for why tumors become so complex and heterogeneous so quickly,” said Michelle Dawson, an assistant professor of molecular pharmacology, physiology and biotechnology at Brown and the study's corresponding author. “By understanding the physical properties of this weird population of cells we might identify a new way to eliminate them. Patients will benefit from that.”
Dawson, who is also an assistant professor of engineering with an appointment in Brown's Center for Biomedical Engineering, worked with graduate student Botai Xuan and two undergraduate students on the study, which focused on a common strain of triple negative breast cancer, an extremely aggressive and hard-to-eradicate kind of breast cancer.
They found that 2-5 percent of cells from this breast cancer strain were polyploidal giant cancer cells with four, eight or sixteen copies of each chromosome, instead of the normal two. The cells with more chromosomes were proportionally larger, which is similar to polyploidal cells in other organisms.
Commercially available strawberries, for example, tend to be much larger than wild strawberries because the cells of commercial varieties have eight copies of each chromosome. After treating the breast cancer cells with a common chemotherapy, the team found three to 10 times more giant cancer cells. This both confirmed that the giant cells were more drug resistant and gave the researchers more giant cells to study.
Then Xuan, first author on the paper, injected nano-sized fluorescent beads into the cancer cells ¾ both polyploidal giant cells and normal ¾ using a specialized technique involving high pressure helium gas. He found that the beads moved about twice as slow inside the giant cells, indicating the cells were stiffer. This stiffness allows the giant cells to get so big, Dawson said.
The research also found that giant cells had more actin, a biopolymer that forms wire-cable-like structures inside cells to help give the cells their shape and allow them to move. When cancer cells move, they can spread or metastasize, a word no patient wants to hear. Giant cancer cells move differently than standard cancer cells too. Like the allegorical tortoise, they move slower than other cancer cells, but go further.
The Dawson Lab tested a drug that interferes with actin and found it softened the giant cancer cells, but Dawson cautioned this would not be a possible treatment for triple negative breast cancer, as it would turn a hypothetical patient into mush. However, a next step for her research is to look at the giant cancer cells at the molecular level to try to find specific differences in order to develop a targeted treatment.
“This first paper really just gave us a lot of structural information,” Dawson said, adding they need to do more research to understand any differences between polyploidal giant cancer cells found before chemotherapy, polyploidal giant cancer cells formed during treatment and the daughter cells they “bud off” in a very atypical manner.
They are also going to look for polyploidal giant cancer cells in samples from patients.
Though the study focused on giant cancer cells found in a strain of triple negative breast cancer, they have found giant cancer cells in other kinds of breast cancer, as well as strains of ovarian and prostate cancer.
“The giant cancer cells break all the cancer rules — they are stiffer, they are larger, they have a very abnormal and non-polarized cell structure — and they can move a long way,” Dawson said. “Without basic science research, we don't get creative new ideas that lead to breakthrough treatments for patients.”
###
Other authors on the study were Deepraj Ghosh, Emily Cheney and Elizabeth Clifton. Funding was provided by National Institute of Health NIGMS through COBRE Center for Cancer Research Development (P30 GM110750).
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



