First synthetic tissue model developed in which blood vessels can grow
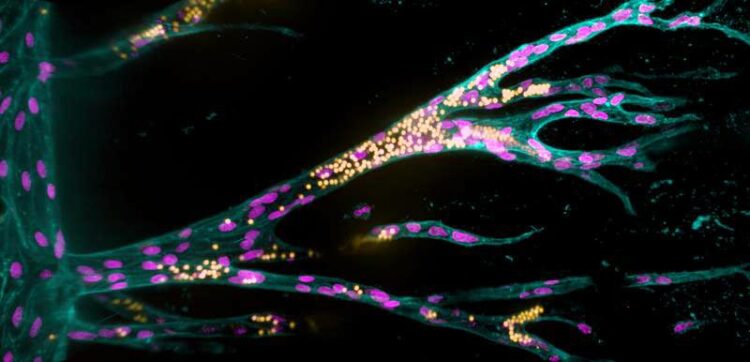
Growing from a parent blood vessel (upright on the left), endothelial cells (pink nuclei) form new blood vessels in a synthetic hydrogel. The fluorescent beads (yellow) simulate blood flow.
(c) Jifeng Liu, MPI Münster / Liu et al./Nat Comm 2021
A research team headed by biomedical engineer Dr Britta Trappmann from the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster, Germany, has developed a cell culture system in which, for the first time, a functional blood vessel system is able to grow within a framework made of synthetic material. The team investigated which material properties promote individual parameters of vessel formation – a step towards the futuristic vision of implantable artificial tissues. The study has been published in the journal “Nature Communications”.
Using lab-created tissue to heal or replace damaged organs is one of the great visions for the future of medicine. Synthetic materials could be suitable as scaffolding for tissue because, unlike natural tissues, they remain stable in the organism long enough for the body to form new natural structures. A fundamental requirement for functional tissue is that blood vessels must be able to grow in them and connect to the organism’s vascular system, so that the tissue is properly supplied with oxygen and nutrients. However, until now, almost nothing has been known about which material properties promote the growth of blood vessels.
A team headed by biomedical engineer Dr Britta Trappmann from the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster, Germany, has developed a cell culture system in which, for the first time, a functional blood vessel system is able to grow within a framework made of synthetic materials. The scientists, working in a special hydrogel with properties they can change in a controlled manner, first grew a parent blood vessel from human blood vessel lining cells. They then investigated how the material properties of the artificial cell environment influenced the formation of additional blood vessels and fine-tuned them. Summarizing the key findings, Britta Trappmann highlights that “The synthetic tissue material must activate certain adhesion molecules in the membrane of blood vessel cells so that the cells migrate in groups from the parent vessel and form tubular structures. At the same time, the material must be sufficiently degradable for the cells to form blood vessels of adequate size”. In order to mimic the natural environment of cells, many additional biomolecules and cells would have to be integrated into the model system in later steps – these may be signaling proteins, immune cells or cells to stabilize the blood vessels. “Moreover, the effect of all these factors is linked in natural tissues and varies from organ to organ,” Britta Trappmann explains. Understanding all of this, she says, is a long-term goal but, ultimately, the knowledge might then be used to grow implantable tissues.
In their investigations, Britta Trappmann and her team worked together with colleagues at the University of Münster as well as working groups from Munich and North Carolina. The study was published in the journal “Nature Communications”.
Details on methods and results:
A three-dimensional tissue framework made of hydrogel
In this study, researchers refined a model system that Britta Trappmann developed with colleagues during her time as a postdoc in the USA at Boston and Harvard Universities. It consists of a three-dimensional sugar-based hydrogel into which the scientists make two channels using an acupuncture needle. Each channel has a diameter of 400 micrometres and they run parallel to each other at a distance of approximately one millimetre. In one channel, the scientists seed endothelial cells, which line blood vessels in natural tissues. “The endothelial cells form contacts with each other and attach to their synthetic tissue environment in the channel, thus forming a parent blood vessel after about a day,” explains Britta Trappmann. When this has happened, the scientists deliver a growth factor cocktail of molecules that drive blood vessel growth in natural tissues through the second channel, whereupon the endothelial cells migrate into the hydrogel.
Molecules in the cell membrane set blood vessel formation in motion
The scientists then wanted to find out which properties of the hydrogel determine whether the migrating endothelial cells actually form new blood vessels. They investigated the role played by the activation of so-called adhesion molecules in the cell membrane through which cells adhere to their surrounding environment. The researchers first enriched the hydrogel tissue framework with varying amounts of peptides that activate a certain type of adhesion molecule found in the membrane of endothelial cells called integrins. The higher the concentration of peptides, the more the endothelial cells migrated together through the hydrogel. In contrast, when the scientists blocked integrin function they observed that the cells only migrated individually. In a further step, the team investigated this process looking at two specific integrin subtypes. “We found that integrin αvβ3 is the crucial adhesion molecule that must be activated for endothelial cells to migrate in groups,” Britta Trappmann says. The scientists also showed that collective cell migration is, in turn, a prerequisite for the endothelial cells to form cavities connected to the parent vessel in the next step.
Cells must be free to move in order to form sufficiently large blood vessels
Although the blood vessel cells then formed tubular structures, these were smaller than those in natural tissues. The scientists hypothesized that this could be because the synthetic hydrogel is less degradable than natural tissue and has smaller pores through which the cells can slip. As the hydrogel consists of sugar molecule chains that are crosslinked by certain molecules, the scientists’ solution was to exchange these crosslinker molecules so that the cells could cleave the hydrogel more quickly using the enzymes they release. This allowed the cells to migrate faster and form larger vascular structures.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the Max Planck Society as well as research networks at the University of Münster including the Collaborative Research Centres 1348 “Dynamic Cellular Interfaces” and 1009 “Breaking Barriers” funded by the German Research Foundation, and the “Cells in Motion” research network.
Links
Original publication in “Nature Communications”
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-23644-5
Research group Dr Britta Trappmann at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster
https://www.mpi-muenster.mpg.de/229627/trappmann
Dr Britta Trappmann at the University of Münster’s Cells in Motion Interfaculty Centre
https://www.uni-muenster.de/Cells-in-Motion/people/all/trappmann-b.php
Research focus on “Cell Dynamics and Imaging” at the University of Münster
https://www.uni-muenster.de/forschung/en/profil/schwerpunkt/zelldynamik.html
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Britta Trappmann, Max Planck Research Group leader
Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine
britta.trappmann@mpi-muenster.mpg.de
Additional contact person:
Doris Niederhoff, Research Communications Manager
Cells in Motion Interfaculty Centre, Münster
+49 251 83-49315
doris.niederhoff@uni-muenster.de
Originalpublikation:
Liu J, Long H, Zeuschner D, Räder AFB, Polacheck WJ, Kessler H, Sorokin L, Trappmann B. Synthetic extracellular matrices with tailored adhesiveness and degradability support lumen formation during angiogenic sprouting. Nat Commun 2021 Jun 7;12(1):3402. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23644-5.
Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-23644-5
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.mpi-muenster.mpg.de/643482/20210727-hydrogel-tissue-for-blood-vessel…
https://www.uni-muenster.de/Cells-in-Motion/newsviews/2021/07-27.html
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



