Gamma radiation helps to understand the mesocrystal formation
Different stages of mesocrystal formation
Credit: Nadja Tarakina, Diana Piankova / Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces
Using targeted gamma radiation, researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces have revealed the appearance and the specific role of non-crystalline phases during the formation of mesocrystals – crystals consisting of aligned nanoparticles. Their findings provide fundamental insights for the controlled development and design of new mesocrystalline.
Wouldn’t it be practical if the bricks of a house assembled all by themselves? This has been happening in nature for millions of years in the form of mesocrystals. These fascinating materials combine nanostructural features with the appearance of large crystals because their nanometer-sized particles self-organize into single-crystalline order. Evolutionary optimized structures with outstanding mechanical properties have been created according to this principle, such as mother-of-pearl, eggshells, sea urchin spines and the hard tissue of our bones.
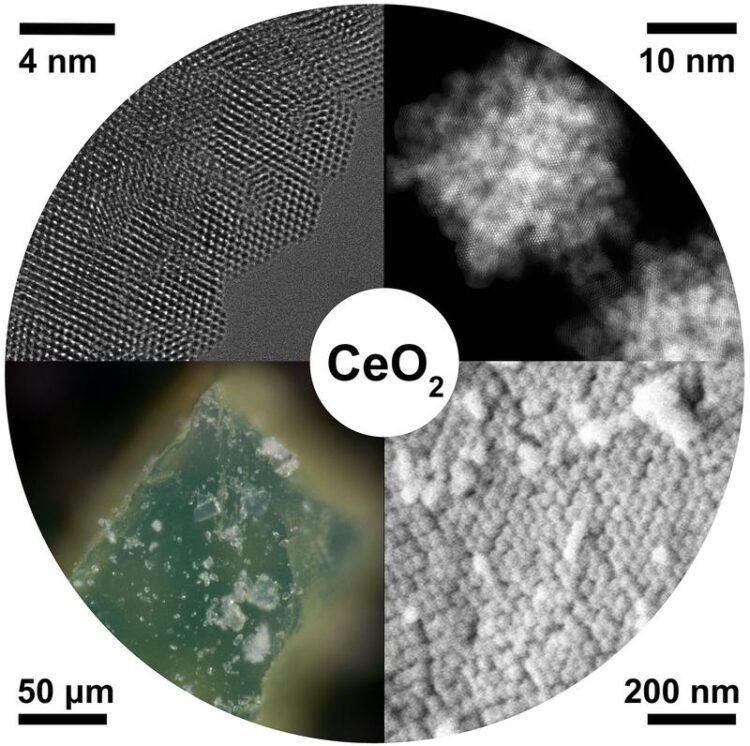
Designing synthetic mesocrystals for different applications requires a detailed understanding of the mechanisms underlying their formation. However, this is complicated because mesocrystals range in size from a few nanometers in the early stages to their final size, which can be visible to the naked eye. “Usually, chemical additives are used to help align the nanoparticles. However, they obscure the initial growth stages of the mesocrystals”, says Dr. Nadja Tarakina, group leader at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces (MPICI).
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute and the KTH Royal Institute of Technology (Sweden) have now synthesized mesocrystals by exposing cerium salt dissolved in water to gamma radiation. “This simple set-up helped us to control the growth more precisely and to minimize the use of chemicals, making observations of the initial stages of the process possible” says Diana Piankova, first author of the study and a doctoral researcher at the MPICI.
The researchers found that amorphous phases (which has no crystalline order) form in the early stages of mesocrystal growth and only then nucleation of primary particles takes place inside this non-crystalline matrix. They also showed that the matrix provides the confinement within which particles align with respect to each other, forming mesocrystals. In analogy to the construction of a house, these amorphous phases play the role of the cement that connects the aligned bricks in the walls.
However, in the case of mesocrystals, the amorphous matrix is also the supplier of the ions that enable the growth of the particles (house bricks) themselves. These crystals constructed from nanoparticles can continue to self-assemble even further after drying and form supracrystals that are visible to the naked eye. Just as an architect may design not a single house but a whole neighborhood so that the houses are oriented in a certain way to serve the specific needs of their inhabitants, this multi-level hierarchical architecture of supracrystals is a fascinating concept for future materials design.
Originalpublikation:
https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202112204
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.mpikg.mpg.de/electron-microscopy (further information about the research group of Dr. Nadja Tarakina)
https://www.mpikg.mpg.de/press-releases (further press releases of the institute)
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



