Gravitational biology
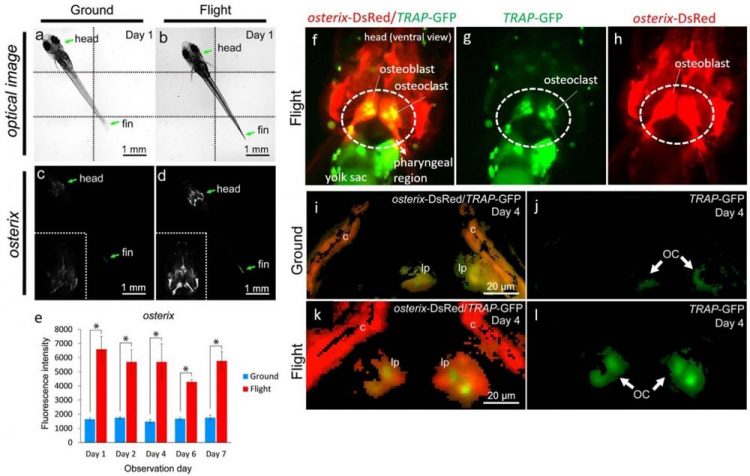
(a-d) Whole-body imaging of the osterix-DsRed transgenic line. The left-side images show the same ground control at day 1; and the right-side images, the same flight medaka at day 1. Arrows point to the head and fin region. All images show ventral views. Montage images were made from 6 captured optical images, divided by dotted lines (a,b). The white region shows an osterix-DsRed fluorescent signal. Embedded views show the enlarged head region (c,d). (e) The fluorescent intensity from day 1 to 7 of observation day constantly increased in the flight group. (f-h) The representative visualizing data for osterix-DsRed/TRAP-GFP in the flight group. All images show ventral views in the head region. (i-l) The merged images were captured by 3D views for osterix-DsRed and TRAP-GFP in the pharyngeal bone region of the double transgenic line. The pharyngeal bone region in the ground control (i) or the flight (k) group at day 4. The image for TRAP-GFP in the pharyngeal bone region of "i" (j) or "k" (l). lp, lower pharyngeal bone; c, cleithrum. GFP signals identify osteoclasts (OC). Credit: Tokyo Institute of Technology
Space travel in a reduced gravity environment can have lasting effects on the body. For example, researches clearly show that astronauts undergo a significant drop in bone mineral density during space missions, but the precise molecular mechanisms responsible for such changes in bone structure are unclear.
Now, Akira Kudo at Tokyo Tech, together with scientists in Japan in support of other countries, performed remotely live-imaging (real time) for fluorescent signals derived from osteoblasts and osteoclasts of medaka fish after only one day of exposure to microgravity aboard the International Space Station (ISS). They found increases in both osteoblast and osteoclast specific promoter-driven GFP and DsRed signals one day after launch, and continued for up to eight days.
In their experiments, the team used four different double medaka transgenic lines focusing on up-regulation of fluorescent signals of osteoblasts and osteoclasts to clarify the effect of gravity on the interaction of osteoblast-osteoclast. They also studied changes in the gene expression in the transgenic fish by so-celled transcriptome analysis.
These findings suggest that exposure to microgravity induced an immediate “dynamic alteration of gene expressions in osteoblasts and osteoclasts.” Namely, these experiments based on real time imaging of medaka from Earth and transcriptome analysis could be the prelude to the establishment of a new scientific areas of research in “gravitational biology”.?
Methodology
The live-imaging of fluorescence microscopy signals from the fish aboard the ISS were monitored remotely from Tsukuba Space Center in Japan.
Live-imaging of osteoblasts showed the intensity of osterix- and osteocalcin-DsRed in pharyngeal bones to increase one day after launch. This increased effect continued for eight days for osterix- and 5 days for osteocalcin.
In the case of osteoclasts, the fluorescent signals observed from TRAP-GFP and MMP9-DsRed increased significantly on the fourth and sixth days after launch.
The fluorescent analysis was complimented by using transcriptome analysis to measure gene expression in the transgenic fish. The researchers state that, “HiSeq from pharyngeal bones of juvenile fish at day 2 after launch showed up-regulation of 2 osteoblast- and 3 osteoclast- related genes”.
Also, transcription of the “nucleus” was found to be significantly enhanced based on whole body gene ontology analysis of RNA-Seq, with the researchers observing transcription-regulators to be more up-regulated at day 2 compared with during day 6.
Finally, Kudo and the team identified 5 genes: (c-fos and jun-b, pai-1 and ddit4, and tsc22d3) that were all up-regulated in the whole-body on days 2 and 6, and in the pharyngeal bone on day 2.
Background
Live in so-called 'microgravity' environments — where the force of gravity is considerably less than on Earth — can cause significant problems for the human body. Astronauts who spend a number of months in space have been shown to suffer from reduced bone mineral density, leading to skeletal problems. Surprisingly, the loss of calcium starts at least 10 days after launch in astronauts in Skylab Flights, as to symptoms that appear early in orbit.
The precise molecular mechanisms responsible for loss of bone density are not yet fully understood. The current study by Kudo and his team is a major step towards uncovering the mechanisms governing changes in bone structure immediately after the onset of microgravity, when bone loss is triggered. By remote live-imaging from Tsukuba Space Center of the behavior of medaka on board the ISS, they found significant increases in both osteoblast and osteoclast specific promoter-driven GFP and DsRed after exposure to microgravity. The findings imply that changes in osteoblasts and osteoclasts occur very soon after launch.
Future
In the next space experiment, Kudo and colleagues will clarify the role of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) on cells in microgravity.
Media Contact
Emiko Kawaguchi
media@jim.titech.ac.jp
81-357-342-975
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



