Harmful protein waste in the muscle
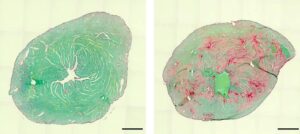
After experimental therapy (right), there are significantly fewer protein aggregates (marked in green) and damage in the myocardium compared with control animals (left).
© Kathrin Graf-Riesen/UKB
An international team of researchers has identified the cause of a rare, severe muscle disease. According to these findings, a single spontaneously occurring mutation results in the muscle cells no longer being able to correctly break down defective proteins. As a result, the cells perish. The condition causes severe heart failure in children, accompanied by skeletal and respiratory muscle damage. Those affected rarely live beyond the age of 20. The study also highlights experimental approaches for potential treatment. Whether this hope will be fulfilled, however, will only become clear in a few years. The results are published in the journal Nature Communications.
An international team of researchers led by the University of Bonn has identified the cause of a rare, severe muscle disease. According to these findings, a single spontaneously occurring mutation results in the muscle cells no longer being able to correctly break down defective proteins. As a result, the cells perish. The condition causes severe heart failure in children, accompanied by skeletal and respiratory muscle damage. Those affected rarely live beyond the age of 20. The study also highlights experimental approaches for potential treatment. Whether this hope will be fulfilled, however, will only become clear in a few years. The results are published in the journal Nature Communications.
© Kenichi Kimura/UKB
Anyone who has ever snapped a spoke on their bike or broken down with their car knows that mechanical stresses sooner or later result in damage that needs to be repaired. This also applies to the human musculature. “With each movement, structural proteins are damaged and have to be replaced,” explains adjunct professor Dr. Michael Hesse from the Institute of Physiology at the University of Bonn, who led the study together with his colleague Prof. Dr. Bernd Fleischmann.
The defective molecules are normally broken down in the cell and their components are then recycled. An important role in this complex process is played by a protein called BAG3. The results of the new study show how important this is: The researchers were able to demonstrate that a single change in the genetic blueprint of BAG3 results in a fatal disease.
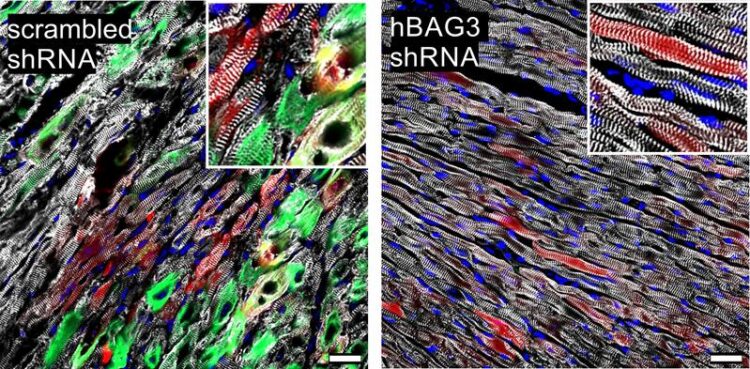
“The mutation causes BAG3 to form insoluble complexes with partner proteins that grow larger and larger,” Hesse says. This brings the repair processes to a standstill – the muscles become less and less efficient. Moreover, toxic levels of proteins accumulate over time, eventually resulting in the death of the muscle cell. “The consequences are usually first seen in the heart,” Hesse says. “There, muscle is successively replaced by scar tissue. This causes the heart’s elasticity to decrease until it can barely pump blood.”
Affected individuals therefore usually require a heart transplant in childhood. Even this measure only provides temporary relief, as the disease also affects the skeletal and respiratory muscles. As a result, sufferers often die at a young age.
Very rare condition, therefore little research
The lethal mutation can arise spontaneously during embryo development. Fortunately, this is a very rare occurrence: There are probably only a few hundred affected children worldwide. However, due to its rarity, the disease has received little research attention to date. “Our study now takes us a great deal further,” stresses Bernd Fleischmann.
This is because the researchers have succeeded for the first time in replicating the disease in mice and using the new animal model to identify its causes. This allows it to be researched better than before – also with regard to possible therapies. Maybe the effect of the mutation can at least be reduced. Humans have two versions of each gene, one from the mother and the other from the father. This means that even if one version of BAG3 mutates during embryo development, there is still a second gene that is intact.
Unfortunately, however, the defective BAG3 also clumps with its intact siblings. The mutation in one of the genes is therefore sufficient to stop the breakdown of the defective muscle proteins. However, if the mutated version could be eliminated, the repair should work again. It would also prevent the massive accumulation of proteins in the cell that eventually results in its death.
There are indeed methods to specifically inhibit the activity of individual genes. “We used one of them to treat the sick mice,” explains Kathrin Graf-Riesen of the Institute of Physiology, who was responsible for most of the experiments along with Dr. Kenichi Kimura and her colleague Dr. Astrid Ooms. The animals treated in this way then showed significantly fewer symptoms. Whether this approach can be transferred to humans, however, remains the subject of further research.
Participating institutions and funding:
In addition to the Institute of Physiology I, the Institute for Cell Biology of the University of Bonn and the Clinic for Cardiac Surgery of the University Hospital Bonn were involved in the study. The partners also include Forschungszentrum Jülich, the Universities of Münster, Freiburg and Cologne, as well as Stanford University in the USA and the University of Tsukuba in Japan. The study was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), including the research group “Mechanical Stress Protection”.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
PD Dr. Michael Hesse
Institut für Physiologie I der Universität Bonn
Telephone: +49-228/6885233
E-mail: mhesse1@uni-bonn.de
Prof. Dr. Bernd Fleischmann
Institut für Physiologie I der Universität Bonn
Telephone: +49-228/6885200
E-Mail: bernd.fleischmann@uni-bonn.de
Originalpublikation:
Kenichi Kimura et al: Overexpression of human BAG3P209L in mice causes restrictive cardiomyopathy. Nature Communications, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23858-7
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



