Helpers in the Assembly of Cellular “Protein Factories”
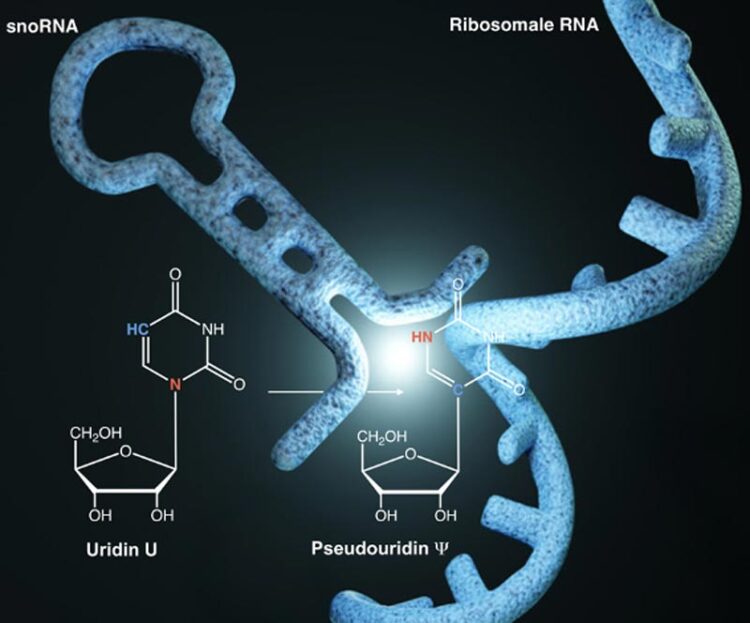
In what is known as pseudouridylation, an RNA module in the long ribosomal RNA chain (rRNA; at right) is modified This process is triggered by a short snoRNA (at left), which guides the modifying enzyme to the selected RNA base of the rRNA. The flash of light shows the enzyme-catalysed conversion of the selected uridine nucleoside into a pseudouridine nucleoside. Both modules are depicted in their biochemical structure. | © Research group Ed Hurt
Heidelberg researchers investigate the earliest steps of ribosome development.
Ribosomes are the nanomachines of the cell whose task is the correct synthesis of proteins. Researchers at the Heidelberg University Biochemistry Center are studying the emergence of these “protein factories”, also known as ribosomes. Led by Prof. Dr Ed Hurt, they have decoded the special role of a heretofore unexplored biogenesis factor in the maturation of precursor ribosomes. The research results, obtained in close cooperation with colleagues of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, were published in the journal “Cell Reports”.
Every cell has a number of these nanomachines that act as protein factories manufacturing vital proteins with various tasks for the organism. A functional ribosome consists of two subunits that are assembled during formation by helper proteins – so-called biogenesis factors. The ribonucleic acids (RNA) and proteins are united into precursors and later complete ribosomes. This process begins in the cell nucleus with the manufacture of a long RNA chain. Step by step, the chain is biochemically altered at selected RNA modules, whereby short RNA molecules known as snoRNAs – small nucleolar RNAs – guide the required enzymes to the selected RNA bases. The precursor RNA chain is then trimmed and finally embellished with ribosomal proteins. “Until now it was unclear when the individual modules are modified and how these modifications are coupled with other maturation steps,” explains Ed Hurt, Senior Professor at the Heidelberg University Biochemistry Center (BZH).
Working with researchers at the Gene Center of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, the Heidelberg scientists were able to demonstrate how a previously unstudied biogenesis factor called Cms1 temporally coordinates the maturation of precursor ribosomes. A highly specific, local chemical change in the ribosomal RNA takes place in the earliest stages of ribosome production. “At this point in time, the RNA is not yet folded and compressed and is therefore accessible for modification by enzymes, which is not possible later in the mature and compact ribosome,” explains Prof. Hurt. In this process, there is an interaction between biogenesis factor Cms1 and a specific area of the still immature RNA. “The central function of Cms1 is to prevent the bonding of other biogenesis factors until the RNA is chemically altered at specific sites,” says Dr Benjamin Lau, a research assistant on Prof. Hurt’s team.
With their findings on the mechanisms leading to functional ribosomes, the researchers also hope to gain a better understanding of diseases such as ribosomopathies, which are based on defective maturation processes. According to Prof. Hurt, there are also clear indications that ribosomal RNA modifications could play a role in the development of cancer. Cancer cells depend on the accelerated production of ribosomes, explains the Heidelberg researcher.
The research work was conducted in the context of Prof. Hurt’s ERC Advanced Grant, a highly endowed grant from the European Research Council.
Contact:
Heidelberg University
Communications and Marketing
Press Office, phone +49 6221 54-2311
presse@rektorat.uni-heidelberg.de
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr Ed Hurt
Heidelberg University Biochemistry Center
Phone +49 6221 54-4173
ed.hurt@bzh.uni-heidelberg.de
Originalpublikation:
B. Lau, O. Beine-Golovchuk, M. Kornprobst, J. Cheng, D. Kressler, B. Jády, T. Kiss, R. Beckmann, E. Hurt: Cms1 coordinates stepwise local 90S pre-ribosome assembly with timely snR83 release. In: Cell Reports 41:111684 (2022). doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111684
Weitere Informationen:
http://www.bzh.db-engine.de/seniorprofessor/7/Ed%20Hurt – Ed Hurt research group
https://bzh.db-engine.de – Biochemistry Center
https://www.uni-heidelberg.de/en/newsroom/helpers-in-the-assembly-of-cellular-protein-factories
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



