How cellular structure orchestrates immunologic memory
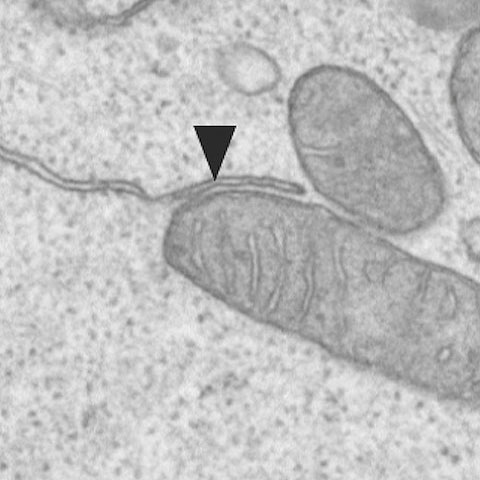
Example of a connection between a mitochondrium and the endoplasmic reticulum. These connections enable the memory CD8 T-cells to protect us quickly from infections.
The human body’s immune system remembers disease-causing pathogens and can react more quickly in case of renewed contact. Vaccines are a prime example of how immunologic memory can protect us from infectious diseases.
In terms of its function and effect, immunologic memory is well understood – an individual remains healthy despite being exposed to the pathogen. However, the specific cellular structures that enable immunologic memory were previously unknown.
An international group of researchers led by Professor Christoph Hess from the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel have now found a structure that accounts for the rapid immunologic memory of particular immune cells (CD8+ memory T cells): these important memory cells form multiple connections between mitochondria – the powerhouses of cells – and the endoplasmic reticulum, the site of protein production.
Rapid immune response
At these contact sites, the rapid immune memory response is literally “orchestrated”, say the researchers. The memory cells concentrate all the signal transmission molecules and enzymes necessary for a rapid immune response here – and so are prepared when the organism is once again exposed to the disease-causing pathogen. This allows the body to quickly protect itself against the infection.
Original source
Glenn R. Bantug, Marco Fischer, Jasmin Grählert, Maria L. Balmer, Gunhild Unterstab, Leyla Develioglu, Rebekah Steiner, Lianjun Zhang, Ana S.H. Costa, Patrick M. Gubser, Anne-Valérie Burgener, Ursula Sauder, Jordan Löliger, Réka Belle, Sarah Dimeloe, Jonas Lötscher, Annaïse Jauch, Mike Recher, Gideon Hönger, Michael N. Hall, Pedro Romero, Christian Frezza, and Christoph Hess
Mitochondria–Endoplasmic Reticulum contact sites function as immunometabolic hubs that orchestrate the rapid recall response of memory CD8 T cells
Immunity (2018), doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.02.012
Further Information
Prof. Dr. Christoph Hess, University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine, Immunobiology, phone: +41 61 328 68 30, e-mail: chess@uhbs.ch
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/How-cellular-structure-or…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



