How mother-of-pearl self-assembles into a perfect structure
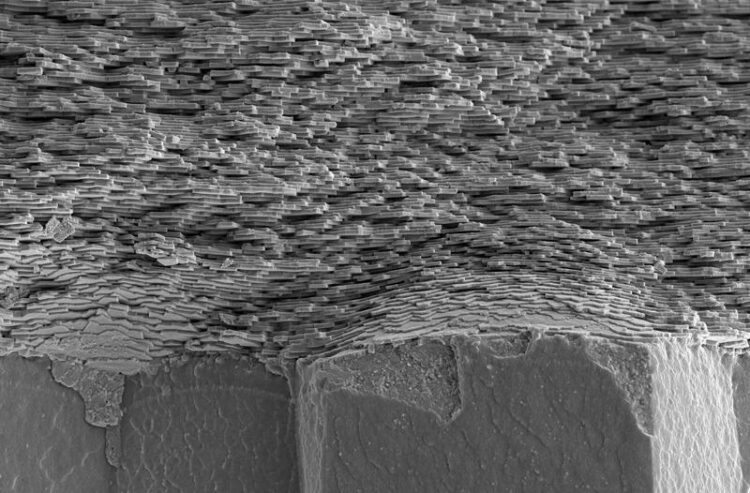
A cross-section through a shell showing the periodically layered nacre on top of a prismatic shell structure.
Image: Igor Zlotnikov
The strength and beauty of mother-of-pearl, also known as nacre, comes from its remarkably regular and uniform architecture. Until now, it was unclear how this intricate structure could be built by a multitude of single cells, all secreting materials at different locations at the same time. In a new study published in Nature Physics, researchers from the B CUBE – Center for Molecular Bioengineering at TU Dresden and European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Grenoble describe, for the first time, that structural defects in self-assembling nacre attract and cancel each other out, eventually leading to a perfect periodic structure.
Mollusks build shells to protect their soft tissues from predators. Nacre, also known as the mother of pearl, has an intricate, highly regular structure that makes it an incredibly strong material. Depending on the species, nacres can reach tens of centimeters in length. No matter the size, each nacre is built from materials deposited by a multitude of single cells at multiple different locations at the same time. How exactly this highly periodic and uniform structure emerges from the initial disorder was unknown until now.
Nacre formation starts uncoordinated with the cells depositing the material simultaneously at different locations. Not surprisingly, the early nacre structure is not very regular. At this point, it is full of defects.
“In the very beginning, the layered mineral-organic tissue is full of structural faults that propagate through a number of layers like a helix. In fact, they look like a spiral staircase, having either right-handed or left-handed orientation,” says Dr. Igor Zlotnikov, research group leader at the B CUBE – Center for Molecular Bioengineering at TU Dresden.
“The role of these defects in forming such a periodic tissue has never been established. On the other hand, the mature nacre is defect-free, with a regular, uniform structure. How could perfection emerge from such disorder?”
The researchers from the Zlotnikov group collaborated with the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Grenoble to take a very detailed look at the internal structure of the early and mature nacre. Using synchrotron-based holographic X-ray nano-tomography the researchers could capture the growth of nacre over time. “Nacre is an extremely fine structure, having organic features below 50 nm in size. Beamline ID16A at the ESRF provided us with an unprecedented capability to visualize nacre in three-dimensions,” explains Dr. Zlotnikov.
“The combination of electron dense and highly periodical inorganic platelets with delicate and slender organic interfaces makes nacre a challenging structure to image. Cryogenic imaging helped us to obtain the resolving power we needed,” explains Dr. Pacureanu from the X-ray Nanoprobe group at the ESRF.
The analysis of data was quite a challenge. The researchers developed a segmentation algorithm using neural networks and trained it to separate different layers of nacre. In this way, they were able to follow what happens to the structural defects as nacre grows.
The behavior of structural defects in a growing nacre was surprising. Defects of opposite screw direction were attracted to each other from vast distances. The right-handed and left-handed defects moved through the structure, until they met, and cancelled each other out. These events led to a tissue-wide synchronization. Over time, it allowed the structure to develop into a perfectly regular and defect-free.
Periodic structures similar to nacre are produced by many different animal species. The researchers think that the newly discovered mechanism could drive not only the formation of nacre but also other biogenic structures.
Dr. Igor Zlotnikov is a leader of a multidisciplinary group at the B CUBE, TU Dresden. The group studies the interplay between physics of materials and cellular control. The Zlotnikov group implements state-of-the-art techniques from a large spectrum of fields in life and physical sciences to address the fundamental question of how the nature uses thermodynamic principles to generate complex structures. The group is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF; grant 03Z22EN11).
B CUBE – Center for Molecular Bioengineering was founded as a Center for Innovation Competence within the initiative “Unternehmen Region” of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. It is part of the Center for Molecular and Cellular Bioengineering (CMCB). B CUBE research focuses on the investigation of living structures on a molecular level, translating the ensuing knowledge into innovative methods, materials and technologies.
Web: www.tu-dresden.de/bcube
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Igor Zlotnikov
Tel: +49 (0) 351 463 43090
Email: igor.zlotnikov@tu-dresden.de
Webpage: www.tu-dresden.de/bcube
Originalpublikation:
Maksim Beliaev, Dana Zoellner, Alexandra Pacureanu, Paul Zasklansky, and Igor Zlotnikov: Dynamics of Topological Defects and Structural Synchronization in a Forming Periodic Tissue. Nature Physics (January 2021)
doi: 10.1038/s41567-020-01069-z https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-020-01069-z
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



