Human MAIT cells sense the metabolic state of enteric bacteria
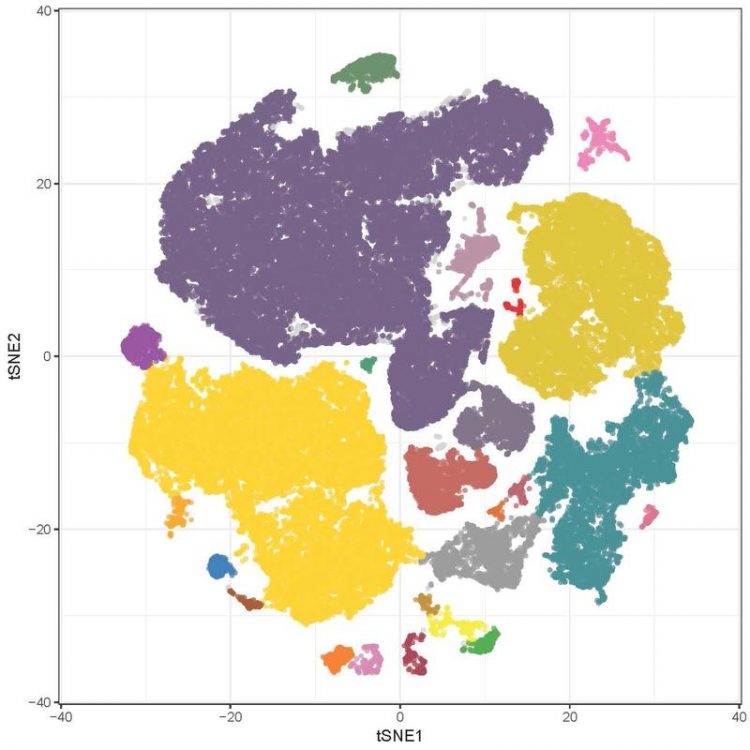
Clusters of MAIT cells in human blood and colon biopsies. Subpopulations of these defense cells group into colored "continents" according to the markers expressed by the cells. Department of Biomedicine, Tobias Rutishauser
It is known that the metabolites of bacteria influence the composition and function of immune cells resident within the gut. These defense cells include MAIT cells (mucosal-associated invariant T cells), which were only recently discovered and are naturally abundant in the gastrointestinal mucosa, skin liver, and blood. These cells are specialized in recognizing the microorganisms living in every human being and monitoring their activities.
Different populations in gut vs. blood
A group led by Prof. Dr. Gennaro De Libero from the University of Basel and PD Dr. Petr Hruz from the University Hospital of Basel have investigated how MAIT cell activation and function is influenced by bacterial metabolites produced in normal colon. The study revealed that distinct populations of MAIT cells are located in the human intestinal mucosa. These populations were identified in gut biopsies using highly innovative methods and bioinformatics analyses.
Result: MAIT cells are present in variable states of alert and rest, in accordance with the metabolic state of intestinal bacterial flora. The defense cells are most frequently stimulated by bacteria grown under low-oxygen and slow growth-phase – conditions such as those found in the large intestine. MAIT cells can then directly influence local inflammation but also tissue healing and cell fitness in the gut by producing different messenger substances.
“Fine balance”
“Our results show that there is a fine balance occurring in the gut between microbial growth conditions, the production of stimulating metabolites and the response of MAIT defense cells,” state the researchers. The metabolism of microbes in the intestine constantly adapts to changing host conditions. By detecting the metabolic state of enteric bacteria, MAIT cells can potentiate their function in mucosal immunosurveillance.
Original source
Mathias Schmaler et al.
Modulation of bacterial metabolism by the microenvironment controls MAIT cell stimulation
Mucosal Immunology (2018), doi: 10.1038/s41385-018-0020-9
Further information
Prof. Dr. Gennaro De Libero, University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine, phone: +41 61 265 23 65, email: gennaro.delibero@unibas.ch
Dr. Lucia Mori, University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine, phone: +41 61 265 23 27, email: lucia.mori@unibas.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



