Injections for diabetes, cancer could become unnecessary
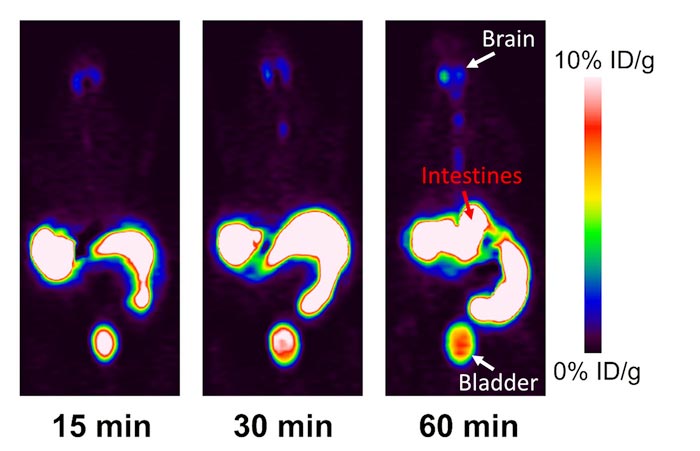
PET scan images show orally administered EPP6 accumulated in the intestines and made its way into the brain and bladder through blood circulation.
Credit: Min Xue/UCR
Hate needles? These researchers do too.
Researchers at UC Riverside are paving the way for diabetes and cancer patients to forget needles and injections, and instead take pills to manage their conditions.
Some drugs for these diseases dissolve in water, so transporting them through the intestines, which receive what we drink and eat, is not feasible. As a result, these drugs cannot be administered by mouth. However, UCR scientists have created a chemical “tag” that can be added to these drugs, allowing them to enter blood circulation via the intestines.
The details of how they found the tag, and demonstrations of its effectiveness, are described in a new Journal of the American Chemical Society paper.
The tag is composed of a small peptide, which is like a protein fragment. “Because they are relatively small molecules, you can chemically attach them to drugs, or other molecules of interest, and use them to deliver those drugs orally,” said Min Xue, UCR chemistry professor who led the research.
Xue’s laboratory was testing something unrelated when the researchers observed these peptides making their way into cells.
“We did not expect to find this peptide making its way into cells. It took us by surprise,” Xue said. “We always wanted to find this kind of chemical tag, and it finally happened serendipitously.”
This observation was unexpected, Xue said, because previously, the researchers believed that this type of delivery tag needed to carry positive charges to be accepted into the negatively charged cells. Their work with this neutral peptide tag, called EPP6, shows that belief was not accurate.
Testing the peptide’s ability to move through a body, the Xue group teamed up with Kai Chen’s group in the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California and fed the peptide to mice. Using a PET scan — a technique similar to a whole-body X-ray that is available at USC, the team observed the peptide accumulating in the intestines, and documented its ultimate transfer into the animals’ organs via the blood.
Having proven the tag successfully navigated the circulatory systems through oral administration, the team now plans to demonstrate that the tag can do the same thing when attached to a selection of drugs. “Quite compelling preliminary results make us think we can push this further,” Xue said.
Many drugs, including insulin, must be injected. The researchers are hopeful their next set of experiments will change that, allowing them to add this tag to a wide variety of drugs and chemicals, changing the way those molecules move through the body.
“This discovery could lift a burden on people who are already burdened with illness,” Xue said.
Journal: Journal of the American Chemical Society
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c07420
Article Title: Hydroxyl-Rich Hydrophilic Endocytosis-Promoting Peptide with No Positive Charge
Article Publication Date: 27-Oct-2022
Media Contact
Jules Bernstein
University of California – Riverside
Jules.Bernstein@ucr.edu
Office: United States
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



