Innovative Antiviral Defense With New CRISPR Tool
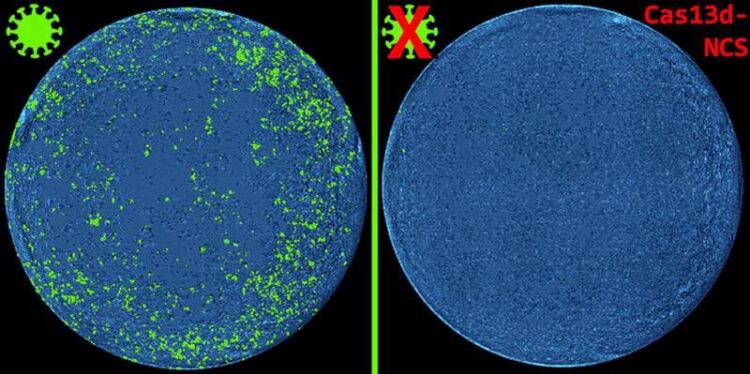
Treatment with Cas13d-NCS prevents the spread of SARS-CoV-2 (green)
(c) Wolfgang Wurst
The rise of RNA viruses like SARS-CoV-2 highlights the need for new ways to fight them. RNA-targeting tools like CRISPR/Cas13 are powerful but inefficient in the cytoplasm of cells, where many RNA viruses replicate. Scientists from Helmholtz Munich and the Technical University Munich (TUM) have devised a solution: Cas13d-NCS. This new molecular tool allows CRISPR RNA molecules that are located within the nucleus of a cell to move to the cytoplasm, making it highly effective at neutralizing RNA viruses. This advancement opens doors for precision medicine and proactive viral defense strategies. The findings were published in Cell Discovery.
As the world prepares for future and ongoing global health threats from RNA viruses such as the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, breakthrough advances in antiviral development are becoming a critical weapon in the fight against these infectious diseases. At the heart of this innovation is the exploration of CRISPR/Cas13 systems, which are known for their programmable capabilities to manipulate RNAs and have become indispensable tools for various RNA targeting applications. However, a significant obstacle has hampered the effectiveness of Cas13d: its restriction to the nucleus of mammalian cells. This drastically limited its utility in cytosolic applications, such as programmable antiviral therapies.
A Potent Antiviral Solution
A scientific team around Prof. Wolfgang Wurst, Dr. Christoph Gruber and Dr. Florian Giesert (Institute of Developmental Genetics at Helmholtz Munich and Chair of Developmental Genetics at TUM), which intensively collaborated with the teams of Dr. Gregor Ebert (Institute of Virology at Helmholtz Munich and at TUM) and of Prof. Andreas Pichlmair (Institute of Virology at TUM), successfully overcame this challenge associated with the cytosolic inactivity of Cas13d. Through careful screening and optimization, the researchers developed a transformative solution: Cas13d-NCS, a novel system capable of transferring nuclear crRNAs into the cytosol. crRNAs, or CRISPR RNAs, are short RNA molecules that guide the CRISPR-Cas complex to specific target sequences for precise modifications. In the cytosol, the protein/crRNA complex targets complementary RNAs and degrades them with unprecedented precision. With remarkable efficiency, Cas13d-NCS outperforms its predecessors in degrading mRNA targets and neutralizing self-replicating RNA, including replicating sequences of Venezuelan equine encephalitis (VEE) RNA virus and several variants of SARS-CoV-2, unlocking the full potential of Cas13d as a programmable antiviral-tool.
Redefining the Landscape of RNA Virus Therapeutics
This important achievement represents a significant step towards combating pandemics and strengthening defenses against future outbreaks. The impact of the study goes beyond traditional antiviral strategies and CRISPR systems and ushers in a new era of precision medicine by enabling the strategic manipulation of subcellular localization of CRISPR-based interventions.
“This breakthrough in antiviral development with Cas13d-NCS marks a pivotal moment in our ongoing battle against RNA viruses,” says Prof. Wolfgang Wurst, coordinator of the study. “This achievement showcases the power of collaborative innovation and human ingenuity in our quest for a healthier and more resilient world.”
About the scientist
Prof. Wolfgang Wurst, Director of the Institute of Developmental Genetics at Helmholtz Munich, Head of of the Chair of Developmental Genetics at TUM, partner of the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and member of the Munich Cluster for Systems Neurology (SyNergy)
About Helmholtz Munich
Helmholtz Munich is a leading biomedical research center. Its mission is to develop breakthrough solutions for better health in a rapidly changing world. Interdisciplinary research teams focus on environmentally triggered diseases, especially the therapy and prevention of diabetes, obesity, allergies, and chronic lung diseases. With the power of artificial intelligence and bioengineering, researchers accelerate the translation to patients. Helmholtz Munich has more than 2,500 employees and is headquartered in Munich/Neuherberg. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, with more than 43,000 employees and 18 research centers the largest scientific organization in Germany. More about Helmholtz Munich (Helmholtz Zentrum München Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Gesundheit und Umwelt GmbH): www.helmholtz-munich.de/en
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
wolfgang.wurst@helmholtz-munich.de
Originalpublikation:
Gruber et al., 2024: Engineered, nucleocytoplasmic shuttling Cas13d enables highly efficient cytosolic RNA targeting. Cell Discovery. DOI: 10.1038/s41421-024-00672-1
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41421-024-00672-1
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



