New Insights into the Signaling Network of the Vital Protein mTOR
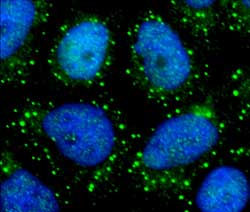
The regulatory protein complex mTORC1 promotes CAD protein oligomerization (Green: CAD oligomers, Blue: DNA).<br>Image: University of Basel/Biozentrum<br>
The research group of Prof. Michael N. Hall at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has now identified a number of new mTOR-regulated proteins, including an enzyme that is essential for the production of the building blocks of DNA. Their results were recently published in the journal «Science».
The protein mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) controls fundamentally important processes such as cell growth and metabolism. As the core component of two complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, it stimulates the production of proteins and fats, and ensures that cells have an adequate energy supply. Dysregulation of the finely-tuned mTOR signaling network is causally involved in the development of serious diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. The search for previously unknown mTOR-regulated proteins could provide new approaches to treat these diseases.
Novel mTOR Target Proteins Identified
Because of the central role of mTOR in the cell, scientists suspect that many of the proteins and processes it controls remain to be discovered. By means of a very advanced technology, the so-called quantitative phosphoproteomics, the research group of Hall has now been able to identify more than 300 new mTOR target proteins which perform a wide range of tasks.
Detailed investigations showed that the mTORC1 stimulates, amongst others, the formation of nucleotides and thus controls the growth and proliferation of cells. Nucleotides are the building blocks of the genetic material and are manufactured in several steps from simple molecules. The first steps in the biosynthesis of nucleotides are mediated by the CAD enzyme. mTORC1 enhances the association of multiple CAD enzymes to form oligomers and thereby stimulates CAD activity and the production of nucleotides.
Many Details Unknown
Although we now understand well how mTOR acts, the current results show that there are still many details which are unknown. The comprehensive investigation of the mTOR-controlled signaling pathways and the effects of regulation deficiencies are enourmously important for the understanding of disease processes and the development of new therapeutic approaches. With their research, Hall and his team add another important piece to the mTOR puzzle.
Original article
Aaron M. Robitaille, Stefan Christen, Mitsugu Shimobayashi, Marion Cornu, Luca L. Fava, Suzette Moes, Cristina Prescianotto-Baschong, Uwe Sauer, Paul Jenoe, and Michael N. Hall (2013)
Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Reveal mTORC1 Activates de Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
Science 1228771, Published online 21 February 2013 | doi: 10.1126/science.1228771
Contact
Prof. Michael N. Hall, University of Basel, Biozentrum, phone: +41 61 267 21 50, email: M.Hall@unibas.ch
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



