Lactate for Brain Energy
Graphics: UZH; Frank Brüderli
In comparison to other organs, the human brain has the highest energy requirements. The supply of energy for nerve cells and the particular role of lactic acid (lactate) has been a matter of intense research for many years. A hypothesis from the 1990’s postulates, that a well-orchestrated collaboration between two cell types, astrocytes and neurons, is the basis of brain energy metabolism.
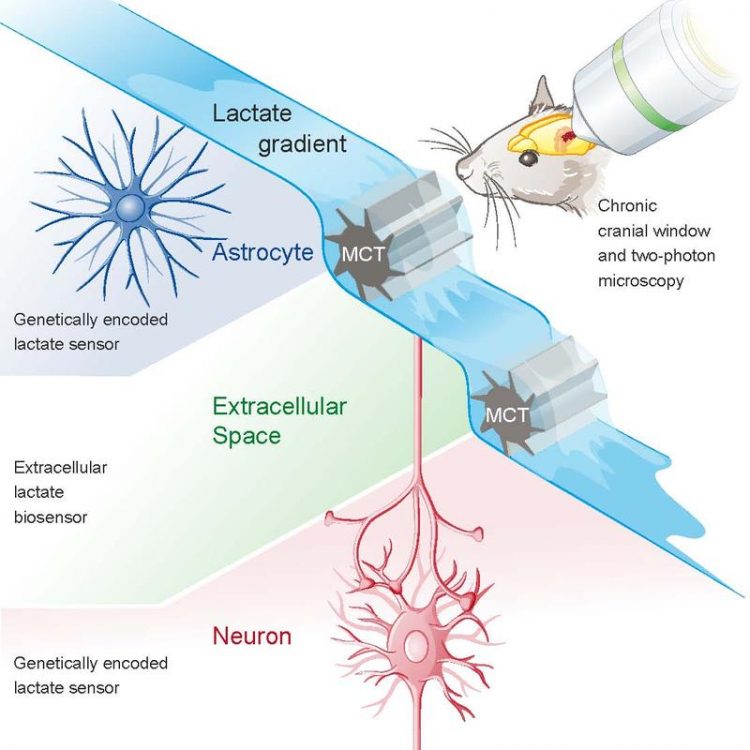
Astrocytes produce lactate, which flows to neurons to cover their high energy needs. Due to a lack of experimental techniques, it remained unclear whether an exchange of lactate existed between astrocytes and neurons. The group of Professor Bruno Weber from the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology now shows that there is a significant concentration gradient of lactate between astrocytes and neurons.
Lactate transport is dependent on concentration
The entry and exit of lactate into and out of cells of the body is concentration dependent and is mediated by a specific lactate transporter (called monocarboxylate transporter or MCT). A typical property of certain transporter proteins is called trans-acceleration. “MCTs can be imagined as revolving doors in a shopping mall, which begin to turn faster when more people enter or exit”, explains Bruno Weber, Professor of Multimodal Experimental Imaging at the University of Zurich.
The researchers made use of this property and accelerated the “revolving doors”. By increasing the extracellular pyruvate concentration, they stimulated the outward transport of lactate. Interestingly, lactate levels only changed in astrocytes but not in neurons. Based on this finding and on results from several control experiments a clear lactate gradient between astrocytes and neurons was confirmed. “Due to the fact that lactate transport by MCTs is a passive transport, such a concentration difference is a necessary condition for a lactate flux to be present”, says Bruno Weber.
The scientists utilized a novel fluorescent protein that binds lactate, thereby changing the amount of light released by the fluorescent molecule. This way they could measure the lactate concentration in single cells. “We expressed the lactate sensor in astrocytes or neurons in the brain of anesthetized mice and measured the fluorescence changes with a special two-photon microscope”, explains Bruno Weber.
More than 20 years after the formulation of the hypothesis that neurons metabolize lactate, the researchers have made an important step closer to final proof of this hypothesis. Bruno Weber closes by stating that “Numerous brain diseases have been associated with metabolic deficits. This underlines the importance of an accurate understanding of the processes contributing to brain energy metabolism at the cellular level”.
Literatur:
P. Mächler, M.T. Wyss, M. Elsayed, J. Stobart, R. Gutierrez, A. von Faber-Castell, V. Kaelin, A. Zuend M. San Martín, I. Romero-Gómez, F. Baeza-Lehnert, S. Lengacher, B.L. Schneider, P. Aebischer, P.J. Magistretti, L.F Barros, B. Weber. In vivo evidence for a lactate gradient from astrocytes to neurons. Cell Metabolism 23, 1–9. November 19, 2015. Doi: org./10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.010
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uzh.ch/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



