
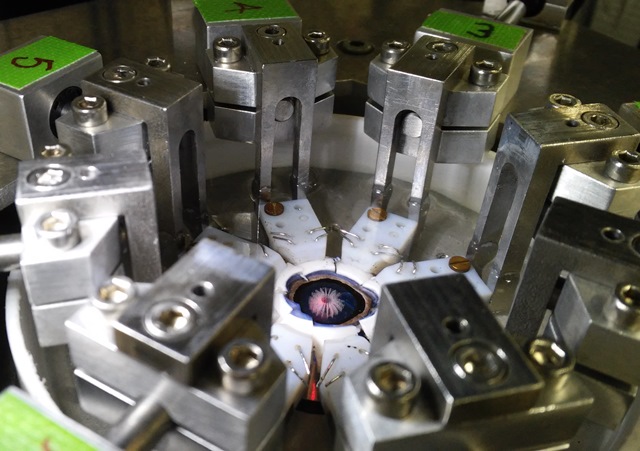
Applying micro-cuts in the lens in a stretcher.
Photo: LZH
The Image-Guided Laser Surgery Group of the Biomedical Optics Department is now developing an experimental setup in which the influence of the micro-cuts on the crystalline lens can be measured.
The special feature of this complex setup is that it can stretch and unstretch a sample crystalline lens, an animal byproduct. Thus, different focus distances of the eye can be simulated. The scientists can measure the changes in the beam path (ray tracing) through the lens both before and after the micro-cuts in the eye have been made.
Prior simulation of the surgery
With the results of these experiments, cutting patterns for the surgical correction of presbyopia can be determined and optimized. The cutting patterns and the measurement results of the experiments will then be entered into a software. This software creates a virtual lens model on which the surgical correction can be simulated prior to the surgery.
The goal of the project is to develop a surgical method in which presbyopia can be corrected in a gentle manner. Additionally, the software should be further developed to customize it for clinical use. It should be able to simulate surgeries a priori in order to improve the results of eye corrections.
Apart from the LZH, the Optimo Medical AG (formerly Integrated Scientific Services AG), which develops the OptimEyesTM software, and the ROWIAK GmbH as manufacturer of the complete laser system are involved in the project.
The project „Ray tracing in ophthalmic finite element models for predicting of visual acuity enhancement“ (RayFEye) is supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SBFI) within the framework of the Eurostars program.












